De novo sequencing and analysis of the transcriptome during the browning of fresh-cut Luffa cylindrica 'Fusi-3' fruits
- PMID: 29145430
- PMCID: PMC5690621
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187117
De novo sequencing and analysis of the transcriptome during the browning of fresh-cut Luffa cylindrica 'Fusi-3' fruits
Abstract
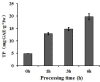
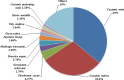
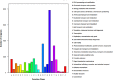
Fresh-cut luffa (Luffa cylindrica) fruits commonly undergo browning. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms regulating this process. We used the RNA-seq technique to analyze the transcriptomic changes occurring during the browning of fresh-cut fruits from luffa cultivar 'Fusi-3'. Over 90 million high-quality reads were assembled into 58,073 Unigenes, and 60.86% of these were annotated based on sequences in four public databases. We detected 35,282 Unigenes with significant hits to sequences in the NCBInr database, and 24,427 Unigenes encoded proteins with sequences that were similar to those of known proteins in the Swiss-Prot database. Additionally, 20,546 and 13,021 Unigenes were similar to existing sequences in the Eukaryotic Orthologous Groups of proteins and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes databases, respectively. Furthermore, 27,301 Unigenes were differentially expressed during the browning of fresh-cut luffa fruits (i.e., after 1-6 h). Moreover, 11 genes from five gene families (i.e., PPO, PAL, POD, CAT, and SOD) identified as potentially associated with enzymatic browning as well as four WRKY transcription factors were observed to be differentially regulated in fresh-cut luffa fruits. With the assistance of rapid amplification of cDNA ends technology, we obtained the full-length sequences of the 15 Unigenes. We also confirmed these Unigenes were expressed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. This study provides a comprehensive transcriptome sequence resource, and may facilitate further studies aimed at identifying genes affecting luffa fruit browning for the exploitation of the underlying mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals potential genes involved in browning of fresh-cut eggplant (Solanum melongena L.).Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 9;11(1):16081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94831-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34373468 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: novel insights into browning-resistant Luffa cylindrica.PeerJ. 2020 Aug 10;8:e9661. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9661. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32864209 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide transcriptome profiling reveals novel insights into Luffa cylindrica browning.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 7;463(4):1243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.093. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26086104
-
Transcriptome analysis of Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem response to infection with Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV).Gene. 2020 May 5;737:144451. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144451. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Gene. 2020. PMID: 32035243
-
De novo sequencing and analysis of the cranberry fruit transcriptome to identify putative genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis, transport and regulation.BMC Genomics. 2015 Sep 2;16(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1842-4. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26330221 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insights into the molecular mechanisms of browning tolerance in luffa: a transcriptome and metabolome analysis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jun 10;16:1530531. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1530531. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40556689 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling reveals potential genes involved in browning of fresh-cut eggplant (Solanum melongena L.).Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 9;11(1):16081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94831-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34373468 Free PMC article.
-
De novo sequencing and analysis of the transcriptome of two highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) cultivars 'Bluecrop' and 'Legacy' at harvest and following post-harvest storage.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 2;16(8):e0255139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255139. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34339434 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: novel insights into browning-resistant Luffa cylindrica.PeerJ. 2020 Aug 10;8:e9661. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9661. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32864209 Free PMC article.
-
Study on browning mechanism of fresh-cut eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) based on metabolomics, enzymatic assays and gene expression.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 25;11(1):6937. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86311-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33767263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nath N, Deka K. Effect of GA3 and KNO3 on seedling establishment of Luffa acutangula (L.) Roxb. Int J Pure App Biosci. 2015; 3(6): 99–103.
-
- Partap S, Kumar A, Sharma NK, Jha KK. Luffa cylindrica: an important medicinal plant. J Nat Prod Plant Res. 2012; 2: 127–134.
-
- Sutharshana V. Protective role of Luffa cylindrical. J Pham Sci Res. 2013; 5: 184–186.
-
- Wang C, Wang H, Lou L, Su X. The identification method of Luffa cylindrical flesh browning. Jiangsu Agric Sci. 2012; 40: 137–138.
-
- Bustos MC, Mazzobre MF, Buera MP. Stabilization of refrigerated avocado pulp: Effect of Allium and Brassica extracts on enzymatic browning. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2015; 61: 89–97.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

