Circulating soluble endoglin modifies the inflammatory response in mice
- PMID: 29145462
- PMCID: PMC5690682
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188204
Circulating soluble endoglin modifies the inflammatory response in mice
Abstract
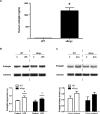
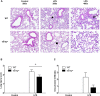
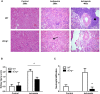
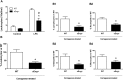
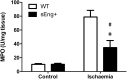
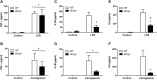
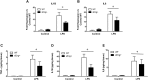
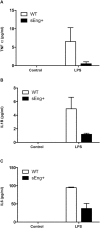
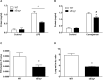
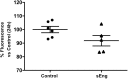
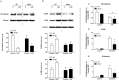
Inflammation is associated with every health condition, and is an important component of many pathologies such as cardiovascular diseases. Circulating levels of soluble endoglin have been shown to be higher in the serum of patients with cardiovascular diseases with a significant inflammatory component. The aim of this study was to evaluate the implication of circulating soluble endoglin in the inflammatory response. For this purpose, a transgenic mouse expressing human soluble endoglin (sEng+) was employed, and three different inflammatory approaches were used to mimic inflammatory conditions in different tissues. This study shows that control sEng+ mice have a normal inflammatory state. The lung and kidney injury induced by the inflammatory agents was reduced in sEng+ mice, especially the intra-alveolar and kidney infiltrates, suggesting a possible reduction in inflammation induced by soluble endoglin. To deepen into this possible effect, the leukocyte number in the bronchoalveolar lavage and air pouch lavage was evaluated and a significant reduction of neutrophil infiltration in LPS-treated lungs and ischemic kidneys from sEng+ with respect to WT mice was observed. Additionally, the mechanisms through which soluble endoglin prevents inflammation were studied. We found that in sEng+ animals the increment of proinflammatory cytokines, TNFα, IL1β and IL6, induced by the inflammatory stimulus was reduced. Soluble endoglin also prevents the augmented adhesion molecules, ICAM, VCAM and E-selectin induced by the inflammatory stimulus. In addition, vascular permeability increased by inflammatory agents was also reduced by soluble endoglin. These results suggest that soluble endoglin modulates inflammatory-related diseases and open new perspectives leading to the development of novel and targeted approaches for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Membrane and soluble endoglin role in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders related to metabolic syndrome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2405-2418. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03701-w. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33185696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Levels of Soluble Endoglin Induce a Proinflammatory and Oxidative-Stress Phenotype Associated with Preserved NO-Dependent Vasodilatation in Aortas from Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet.J Vasc Res. 2016;53(3-4):149-162. doi: 10.1159/000448996. Epub 2016 Oct 8. J Vasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27721318
-
High soluble endoglin levels do not induce endothelial dysfunction in mouse aorta.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0119665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119665. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25768936 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble endoglin modulates the pro-inflammatory mediators NF-κB and IL-6 in cultured human endothelial cells.Life Sci. 2017 Apr 15;175:52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.03.014. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28336397
-
Mediators released from LPS-challenged lungs induce inflammatory responses in liver vascular endothelial cells and neutrophilic leukocytes.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):G1066-76. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00278.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19815624
Cited by
-
High Procalcitonin, C-Reactive Protein, and α-1 Acid Glycoprotein Levels in Whole Blood Samples Could Help Rapid Discrimination of Active Tuberculosis from Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Healthy Individuals.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 28;10(10):1928. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101928. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296203 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Antiangiogenic Factors in Chronic Kidney Disease: Potential Biomarkers of Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 24;19(7):1859. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071859. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29937525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane and soluble endoglin role in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders related to metabolic syndrome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2405-2418. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03701-w. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33185696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anserine reduces mortality in experimental sepsis by preventing methylglyoxal-induced capillary leakage.EBioMedicine. 2025 Apr;114:105644. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105644. Epub 2025 Mar 18. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40107203 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Escherichia coli change the adhesion between neutrophils and endotheliocytes in the experimental bacteremia model.Microb Cell. 2024 Jul 22;11:254-264. doi: 10.15698/mic2024.07.830. eCollection 2024. Microb Cell. 2024. PMID: 39045084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butchar JP, Parsa KVL, Marsh CB, Tridandapani S. Negative regulators of toll-like receptor 4-mediated macrophage inflammatory response. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12[32]:4143–53. - PubMed
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002. December 19;420[6917]:853–9. doi: 10.1038/nature01321 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schmid-Schönbein GW. Analysis of inflammation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8:93–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095708 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura A. Signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines and tumor development. Cancer Sci. 2006. June;97[6]:439–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00197.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Venkatesha S, Toporsian M, Lam C, Hanai J, Mammoto T, Kim YM, et al. Soluble endoglin contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Nat Med. 2006. June;12[6]:642–9. doi: 10.1038/nm1429 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

