Renal failure during chemotherapy: renal biopsy for assessing subacute nephrotoxicity of pemetrexed
- PMID: 29145816
- PMCID: PMC5689204
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3705-7
Renal failure during chemotherapy: renal biopsy for assessing subacute nephrotoxicity of pemetrexed
Abstract
Background: Pemetrexed, a multitargeted antifolate cytotoxic agent, is currently used primarily in combination with cisplatin for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer and for malignant mesothelioma. Acute renal toxicity of pemetrexed has been recently described with polychemotherapy, in which the individual responsibility of each drug is difficult to establish. Only one recent report documents renal involvement in long-term exposed patients.
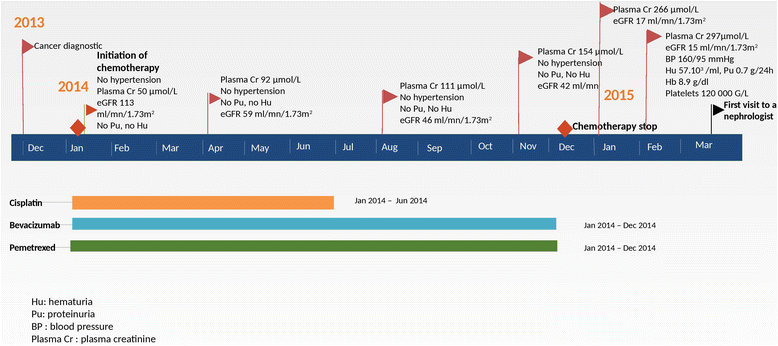
Case presentation: We report on a case of rapidly progressive nephropathy leading to the cessation of platinum salts and the secondary interruption of pemetrexed and bevacizumab. Acute tubular necrosis shown on the renal biopsy could potentially be due to pemetrexed. Persistent severe renal failure after the resumption of all drugs led to new treatment lines with gemcitabine (while the glomerular filtration rate was below 30 ml/min/1.73m2), then followed by Taxol.
Conclusions: The optimal strategy with regard to renal complications in cancer patients is not clear. Acute or chronic loss in renal function generally leads to a new treatment line, possibly impairing the overall success of the treatment. The use of chemotherapy in patients with a glomerular filtration rate below 30 ml/min/1.73m2 is usually associated with an increased risk of side effects when not contraindicated by renal elimination of the drug.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
CARE guidelines/methodology were adhered to.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of her clinical details was obtained from the patient.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pemetrexed-induced acute kidney injury leading to chronic kidney disease.Clin Nephrol. 2014 Dec;82(6):402-6. doi: 10.5414/CN107921. Clin Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24424085
-
Pemetrexed induced acute kidney injury in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: reversible and chronic renal damage.J Nephrol. 2015 Apr;28(2):187-91. doi: 10.1007/s40620-014-0117-5. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 24986522
-
Renal impairment during pemetrexed maintenance in patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: a cohort study.Eur Respir J. 2018 Oct 25;52(4):1800884. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00884-2018. Print 2018 Oct. Eur Respir J. 2018. PMID: 30139775
-
Pemetrexed: a multitargeted antifolate.Clin Ther. 2005 Sep;27(9):1343-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.09.010. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16291410 Review.
-
The efficacy and toxicity of maintenance therapy with bevacizumab plus pemetrexed versus bevacizumab/pemetrexed alone for stage IIIB/IV nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Feb;47(2):157-167. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13534. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 34617297 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy-induced acute kidney injury: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches.Front Nephrol. 2024 Aug 9;4:1436896. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1436896. eCollection 2024. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39185276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chapter 1: Evaluation of kidney function in patients undergoing anticancer drug therapy, from clinical practice guidelines for the management of kidney injury during anticancer drug therapy 2022.Int J Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;28(10):1259-1297. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02372-4. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Int J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37382749 Review.
-
A cross-sectional study of chemotherapy-related AKI.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;77(10):1503-1512. doi: 10.1007/s00228-021-03115-y. Epub 2021 May 15. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33993344
-
Chemical investigation and screening of anti-cancer potential of Syzygium aromaticum L. bud (clove) essential oil nanoemulsion.3 Biotech. 2022 Feb;12(2):49. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03117-2. Epub 2022 Jan 27. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35127304 Free PMC article.
-
The Nephrotoxicity of Drugs Used in Causal Oncological Therapies.Curr Oncol. 2022 Dec 8;29(12):9681-9694. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29120760. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36547174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sassier M, Dugué AE, Clarisse B, et al. Renal insufficiency is the leading cause of double maintenance (bevacizumab and pemetrexed) discontinuation for toxicity to advanced non-small cell lung cancer in real world setting. Lung Cancer. 2015;89(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

