Association of sputum and blood eosinophil concentrations with clinical measures of COPD severity: an analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort
- PMID: 29146301
- PMCID: PMC5849066
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30432-0
Association of sputum and blood eosinophil concentrations with clinical measures of COPD severity: an analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort
Abstract
Background: Increased concentrations of eosinophils in blood and sputum in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) have been associated with increased frequency of exacerbations, reduced lung function, and corticosteroid responsiveness. We aimed to assess whether high eosinophil concentrations in either sputum or blood are associated with a severe COPD phenotype, including greater exacerbation frequency, and whether blood eosinophils are predictive of sputum eosinophils.
Methods: We did a multicentre observational study analysing comprehensive baseline data from SPIROMICS in patients with COPD aged 40-80 years who had a smoking history of at least 20 pack-years, recruited from six clinical sites and additional subsites in the USA between Nov 12, 2010, and April 21, 2015. Inclusion criteria for this analysis were SPIROMICS baseline visit data with complete blood cell counts and, in a subset, acceptable sputum counts. We stratified patients on the basis of blood and sputum eosinophil concentrations and compared their demographic characteristics, as well as results from questionnaires, clinical assessments, and quantitative CT (QCT). We also analysed whether blood eosinophil concentrations reliably predicted sputum eosinophil concentrations. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01969344).
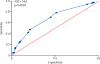
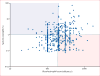
Findings: Of the 2737 patients recruited to SPIROMICS, 2499 patients were smokers and had available blood counts, and so were stratified by mean blood eosinophil count: 1262 patients with low (<200 cells per μL) and 1237 with high (≥200 cells per μL) blood eosinophil counts. 827 patients were eligible for stratification by mean sputum eosinophil percentage: 656 with low (<1·25%) and 171 with high (≥1·25%) sputum eosinophil percentages. The high sputum eosinophil group had significantly lower median FEV1 percentage predicted than the low sputum eosinophil group both before (65·7% [IQR 51·8-81·3] vs 75·7% [59·3-90·2], p<0·0001) and after (77·3% [63·1-88·5] vs 82·9% [67·8-95·9], p=0·001) bronchodilation. QCT density measures for emphysema and air trapping were significantly higher in the high sputum eosinophil group than the low sputum eosinophil group. Exacerbations requiring corticosteroids treatment were more common in the high versus low sputum eosinophil group (p=0·002). FEV1 percentage predicted was significantly different between low and high blood eosinophil groups, but differences were less than those observed between the sputum groups. The high blood eosinophil group had slightly increased airway wall thickness (0·02 mm difference, p=0·032), higher St George Respiratory Questionnaire symptom scores (p=0·037), and increased wheezing (p=0·018), but no evidence of an association with COPD exacerbations (p=0·35) or the other indices of COPD severity, such as emphysema measured by CT density, COPD assessment test scores, Body-mass index, airflow Obstruction, Dyspnea, and Exercise index, or Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease stage. Blood eosinophil counts showed a weak but significant association with sputum eosinophil counts (receiver operating characteristic area under the curve of 0·64, p<0·0001), but with a high false-discovery rate of 72%.
Interpretation: In a large, well characterised cohort of former and current smoking patients with a broad range of COPD severity, high concentrations of sputum eosinophils were a better biomarker than high concentrations of blood eosinophils to identify a patient subgroup with more severe disease, more frequent exacerbations, and increased emphysema by QCT. Blood eosinophils alone were not a reliable biomarker for COPD severity or exacerbations, or for sputum eosinophils. Clinical trials targeting eosinophilic inflammation in COPD should consider assessing sputum eosinophils.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
NEA, ERB, REK, WO’N NP and XL report nothing to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Eosinophils in COPD: are we nearly there yet?Lancet Respir Med. 2017 Dec;5(12):913-914. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30445-9. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Lancet Respir Med. 2017. PMID: 29146300 No abstract available.
-
New Treatment Approaches and Prognostic Biomarkers for Advanced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Potential Associated Cardiovascular Risks.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Apr 1;199(7):913-916. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201804-0659RR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30785763 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hiemstra PS. Altered macrophage function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Annals ATS. 2013;10(Supplement):S180–185. - PubMed
-
- Chung KF. Cytokines in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2001;34:50s–59s. - PubMed
-
- Sethi S, Mahler DA, Marcus P, Owen CA, Yawn B, Rennard S. Inflammation in COPD: implications for management. Am J Med. 2012;125:1162–1170. - PubMed
-
- Singh D, Kolsum U, Brightling CE, Locantore N, Agusti A, Tal-Singer R on behalf of the ECLIPSE investigators. Eosinophilic inflammation in COPD: prevalence and clinical characteristics. Eur Respir J. 2014;44:1697–1700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HHSN268200900019C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900015C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900016C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL137880/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122438/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900018C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900013C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL130627/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL123778/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL137013/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL123594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX000911/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- HHSN268200900017C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200900020C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

