Diabetic foot
- PMID: 29146579
- PMCID: PMC5688746
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.j5064
Diabetic foot
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: We have read and understood BMJ policy on declaration of interests and declare the following: SM, KC, and AK were members of the guideline development group for the standard treatment guideline on the diabetic foot: prevention and management in India, 2016 published by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, government of India. AM provided technical input on methodology to this guideline development group.
Figures
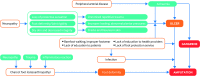
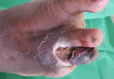
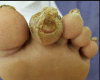
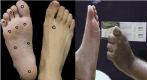

References
-
- Zhang P, Lu J, Jing Y, Tang S, Zhu D, Bi Y. Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis (†). Ann Med 2017;49:106-16. 10.1080/07853890.2016.1231932 pmid:27585063. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schaper NC, Apelqvist J, Bakker K. The international consensus and practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot. Curr Diab Rep 2003;3:475-9. 10.1007/s11892-003-0010-4 pmid:14611743. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeffcoate W, Bakker K. World Diabetes Day: footing the bill. Lancet 2005;365:1527 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66437-9 pmid:15866295. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lazzarini PA, Hurn SE, Fernando ME, et al. Prevalence of foot disease and risk factors in general inpatient populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2015;5:e008544 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008544 pmid:26597864. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA 2005;293:217-28. 10.1001/jama.293.2.217 pmid:15644549. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
