Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Inhibits Pseudoaneurysm Formation After Aortic Patch Angioplasty
- PMID: 29146747
- PMCID: PMC5746454
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310372
Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Inhibits Pseudoaneurysm Formation After Aortic Patch Angioplasty
Abstract
Objective: Pseudoaneurysms remain a significant complication after vascular procedures. We hypothesized that TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) signaling plays a mechanistic role in the development of pseudoaneurysms.
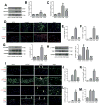
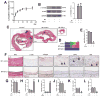
Approach and results: Rat aortic pericardial patch angioplasty was associated with a high incidence (88%) of pseudoaneurysms at 30 days, with increased smad2 phosphorylation in small pseudoaneurysms but not in large pseudoaneurysms; TGF-β1 receptors were increased in small pseudoaneurysms and preserved in large pseudoaneurysms. Delivery of TGF-β1 via nanoparticles covalently bonded to the patch stimulated smad2 phosphorylation both in vitro and in vivo and significantly decreased pseudoaneurysm formation (6.7%). Inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling with SB431542 decreased smad2 phosphorylation both in vitro and in vivo and significantly induced pseudoaneurysm formation by day 7 (66.7%).
Conclusions: Normal healing after aortic patch angioplasty is associated with increased TGF-β1 signaling, and recruitment of smad2 signaling may limit pseudoaneurysm formation; loss of TGF-β1 signaling is associated with the formation of large pseudoaneurysms. Enhancement of TGF-β1 signaling may be a potential mechanism to limit pseudoaneurysm formation after vascular intervention.
Keywords: TGF beta; animal model; nanoparticle; pseudoaneurysm; smad2.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Webber GW, Jang J, Gustavson S, Olin JW. Contemporary management of postcatheterization pseudoaneurysms. Circulation. 2007;115:2666–2674. - PubMed
-
- Klonaris C, Katsargyris A, Papapetrou A, Vourliotakis G, Tsiodras S, Georgopoulos S, Giannopoulos A, Bastounis E. Infected femoral artery pseudoaneurysm in drug addicts: The beneficial use of the internal iliac artery for arterial reconstruction. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:498–504. - PubMed
-
- Belardi P, Noce R. pseudoaneurysm of the right femoral anastomosis from an aorto-femoral dacron bypass. Removal and reconstruction of the artery. Minerva Chir. 1968;23:1066–1074. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan S, Clowes AW. Dacron patch infection after carotid endarterectomy: Case report and review of the literature. Ann Vasc Surg. 2006;20:672–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

