QTL mapping and molecular characterization of the classical D locus controlling seed and flower color in Linum usitatissimum (flax)
- PMID: 29146906
- PMCID: PMC5691222
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11565-7
QTL mapping and molecular characterization of the classical D locus controlling seed and flower color in Linum usitatissimum (flax)
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: QTL mapping and molecular characterization of the classical D locus controlling seed and flower color in Linum usitatissimum (flax).Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 12;8(1):4567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22651-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29531258 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The flowers of flax (linseed) are blue-hued, ephemeral and self-pollinating, and the seeds are typically brown. A century-old interest in natural yellow seed variants and a historical model point to recessive alleles in B1, D and G loci being responsible, but the functional aspects had remained unknown. Here, we characterized the "D" locus by quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and identified a FLAVONOID 3'5' HYDROXYLASE (F3'5'H) gene therein. It does not belong to the F3'5'H clade, but resembles biochemically characterized F3'Hs (flavonoid 3' hydroxylase) but without F3'H activity. The genome lacks other F3'H or F3'H-like genes. The apparent neo-functionalization from F3'H is associated with a Thr498 → Ser498 substitution in a substrate recognition site (SRS). The yellow seed and white flower phenotypes of the classical d mutation was found to be due to one nucleotide deletion that would truncate the deduced product and remove three of the six potential SRS, negatively impacting delphinidin synthesis. Delphinidin is sporadic in angiosperms, and flax has no known pollination syndrome(s) with functional pollinator group(s) that are attracted to blue flowers, raising questions on the acquisition of F3'5'H. The appearance of d allele is suggestive of the beginning of the loss of F3'5'H in this species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


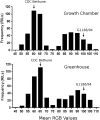
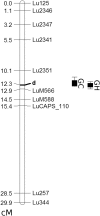
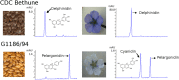

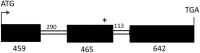


References
-
- Green, A. G. & Dribnenki, J. C. P. Breeding and development of LINOLA (low-linolenic flax). In The Third Meeting of the International Flax Breeding Group. 144–150 (1995).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

