Revisiting the role of interleukin-8 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 29146966
- PMCID: PMC5691131
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15953-x
Revisiting the role of interleukin-8 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
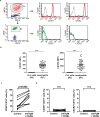
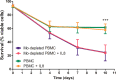
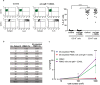
The proliferation and survival of malignant B cells in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) depend on signals from the microenvironment in lymphoid tissues. Among a plethora of soluble factors, IL-8 has been considered one of the most relevant to support CLL B cell progression in an autocrine fashion, even though the expression of IL-8 receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, on leukemic B cells has not been reported. Here we show that circulating CLL B cells neither express CXCR1 or CXCR2 nor they respond to exogenous IL-8 when cultured in vitro alone or in the presence of monocytes/nurse-like cells. By intracellular staining and ELISA we show that highly purified CLL B cells do not produce IL-8 spontaneously or upon activation through the B cell receptor. By contrast, we found that a minor proportion (<0.5%) of contaminating monocytes in enriched suspensions of leukemic cells might be the actual source of IL-8 due to their strong capacity to release this cytokine. Altogether our results indicate that CLL B cells are not able to secrete or respond to IL-8 and highlight the importance of methodological details in in vitro experiments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- di Celle PF, et al. Cytokine gene expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: evidence of constitutive interleukin-8 (IL-8) mRNA expression and secretion of biologically active IL-8 protein. Blood. 1994;84:220–228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

