Origin of the unusually strong and selective binding of vanadium by polyamidoximes in seawater
- PMID: 29146970
- PMCID: PMC5691157
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01443-1
Origin of the unusually strong and selective binding of vanadium by polyamidoximes in seawater
Abstract
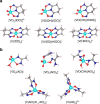
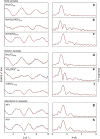
Amidoxime-functionalized polymeric adsorbents are the current state-of-the-art materials for collecting uranium (U) from seawater. However, marine tests show that vanadium (V) is preferentially extracted over U and many other cations. Herein, we report a complementary and comprehensive investigation integrating ab initio simulations with thermochemical titrations and XAFS spectroscopy to understand the unusually strong and selective binding of V by polyamidoximes. While the open-chain amidoxime functionalities do not bind V, the cyclic imide-dioxime group of the adsorbent forms a peculiar non-oxido V5+ complex, exhibiting the highest stability constant value ever observed for the V5+ species. XAFS analysis of adsorbents following deployment in environmental seawater confirms V binding solely by the imide-dioximes. Our fundamental findings offer not only guidance for future optimization of selectivity in amidoxime-based sorbent materials, but may also afford insight to understanding the extensive accumulation of V in some marine organisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
First-Principles Integrated Adsorption Modeling for Selective Capture of Uranium from Seawater by Polyamidoxime Sorbent Materials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Apr 18;10(15):12580-12593. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b17031. Epub 2018 Apr 6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 29580049
-
Successful Coupling of a Bis-Amidoxime Uranophile with a Hydrophilic Backbone for Selective Uranium Sequestration.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Aug 23;9(33):27894-27904. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b04656. Epub 2017 Aug 15. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28752756
-
Theoretical Insights on Improving Amidoxime Selectivity for Potential Uranium Extraction from Seawater.J Phys Chem A. 2022 Jan 27;126(3):406-415. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c08072. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Phys Chem A. 2022. PMID: 35020373
-
Recent developments and challenges in uranium extraction from seawater through amidoxime-functionalized adsorbents.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Oct;30(47):103496-103512. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-29589-0. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37704807 Review.
-
Uranium speciation and bioavailability in aquatic systems: an overview.ScientificWorldJournal. 2002 Mar 15;2:707-29. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2002.130. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002. PMID: 12805996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vanadium for Green Energy: Increasing Demand but With Health Implications in Volcanic Terrains.Geohealth. 2022 Jul 1;6(7):e2021GH000579. doi: 10.1029/2021GH000579. eCollection 2022 Jul. Geohealth. 2022. PMID: 35799914 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Biofouling Polyzwitterion-Poly(amidoxime) Composite Hydrogel for Highly Enhanced Uranium Extraction from Seawater.Gels. 2024 Sep 22;10(9):603. doi: 10.3390/gels10090603. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39330205 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatographic Purification of Lithium, Vanadium, and Uranium from Seawater Using Organic Composite Adsorbents Composed of Benzo-18-Crown-6 and Benzo-15-Crown-5 Embedded in Highly Porous Silica Beads.ACS Omega. 2022 Jul 27;7(31):27410-27421. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02427. eCollection 2022 Aug 9. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35967073 Free PMC article.
-
Amidoxime-Functionalized Macroporous Carbon Self-Refreshed Electrode Materials for Rapid and High-Capacity Removal of Heavy Metal from Water.ACS Cent Sci. 2019 Apr 24;5(4):719-726. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b00130. Epub 2019 Mar 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2019. PMID: 31041392 Free PMC article.
-
Constructing amidoxime-modified porous adsorbents with open architecture for cost-effective and efficient uranium extraction.Chem Sci. 2020 Apr 14;11(18):4747-4752. doi: 10.1039/d0sc00249f. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34122930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nuclear Energy Agency, Uranium: Resources, Production and Demand, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/uranium-2016-en - DOI
-
- Davies RV, Kennedy J, McIlroy RW, Spence R, Hill KM. Extraction of uranium from sea water. Nature. 1964;203:1110–1115. doi: 10.1038/2031110a0. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

