Dendrimers for Ocular Drug Delivery
- PMID: 29147035
- PMCID: PMC5683719
- DOI: 10.1139/cjc-2017-0193
Dendrimers for Ocular Drug Delivery
Abstract
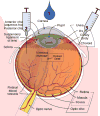
Existing methods of administering ocular drugs are limited in either their safety or efficiency. Nanomedicine therapies have the potential to address this deficiency by creating vehicles that can control drug biodistribution. Dendrimers are synthetic polymeric nanoparticles with a unique highly organized branching structure. In recent years, promising results using dendrimer vehicles to deliver ocular drugs through different routes of administration have been reported. In this review, we briefly summarize these results with emphasis on the dendrimer modifications used to target different ocular structures.
Keywords: dendrimer; nanomedicine; ocular drug delivery.
Figures

References
-
- Aref AA. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017;28(2):169–174. - PubMed
-
- Rein DB. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013;54(14):ORSF18-22. - PubMed
-
- Vellonen KS, Soini EM, del Amo EM, Urtti A. Mol. Pharm. 2016;13(9):2906–2911. - PubMed
-
- Korte JM, Kaila T, Saari MK. Graefe's Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2002;240(6):430. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
