Pemetrexed-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis: A Case Study and Literature Review
- PMID: 29147410
- PMCID: PMC5649774
- DOI: 10.14740/wjon845w
Pemetrexed-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis: A Case Study and Literature Review
Abstract
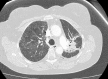
Pemetrexed is a new-generation antifolate drug, now widely used in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We report a case of pemetrexed-induced interstitial pneumonitis, and review the literature of eight previously reported cases. As pemetrexed is now a widely used chemotherapeutic agent, it is important to be aware of rare adverse events related to its administration.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Interstitial pneumonitis; Lung toxicity; Non-small cell lung cancer; Pemetrexed; Treatment-related complication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest in regard to this manuscript. We declare no financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that could inappropriately influence our work.
Figures
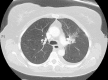
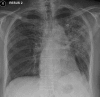
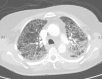
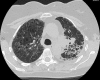
Similar articles
-
Pemetrexed induced pneumonitis.Clin Pract. 2011 Nov 8;1(4):e106. doi: 10.4081/cp.2011.e106. eCollection 2011 Sep 28. Clin Pract. 2011. PMID: 24765347 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Pneumonitis after Treatment with Pemetrexed for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Mar;45(1):74-7. doi: 10.4143/crt.2013.45.1.74. Epub 2013 Mar 31. Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23613674 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial pneumonitis after treatment with pemetrexed: a rare event?Chemotherapy. 2012;58(1):84-8. doi: 10.1159/000336131. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Chemotherapy. 2012. PMID: 22377772
-
Pemetrexed: a multitargeted antifolate.Clin Ther. 2005 Sep;27(9):1343-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2005.09.010. Clin Ther. 2005. PMID: 16291410 Review.
-
Pemetrexed in second line of non-small cell lung cancer.Rev Port Pneumol. 2008 Jul;14 Suppl 2:S21-6. doi: 10.1016/S0873-2159(15)30311-1. Rev Port Pneumol. 2008. PMID: 25967564 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Drug-Related Pneumonitis in Cancer Treatment during the COVID-19 Era.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 2;13(5):1052. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051052. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pemetrexed-induced Interstitial Lung Disease Mimicking Hypersensitivity Pneumonia: A Pathologically Proven Case.Intern Med. 2019 Sep 15;58(18):2679-2682. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2548-18. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 31178492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shih C, Chen VJ, Gossett LS, Gates SB, MacKellar WC, Habeck LL, Shackelford KA. et al. LY231514, a pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-based antifolate that inhibits multiple folate-requiring enzymes. Cancer Res. 1997;57(6):1116–1123. - PubMed
-
- Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, Biesma B, Vansteenkiste J, Manegold C, Serwatowski P. et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(21):3543–3551. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0375. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, Pereira JR, De Marinis F, von Pawel J, Gatzemeier U. et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(9):1589–1597. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.163. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C, Kim JH, Krzakowski M, Laack E, Wu YL. et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2009;374(9699):1432–1440. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61497-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
