Cytotoxic (salen)ruthenium(iii) anticancer complexes exhibit different modes of cell death directed by axial ligands
- PMID: 29147511
- PMCID: PMC5632802
- DOI: 10.1039/c7sc02205k
Cytotoxic (salen)ruthenium(iii) anticancer complexes exhibit different modes of cell death directed by axial ligands
Abstract
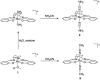
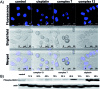
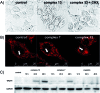
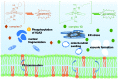
Two novel series of (salen)ruthenium(iii) complexes bearing guanidine and amidine axial ligands were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated for anticancer activity. In vitro cytotoxicity tests demonstrate that these complexes are cytotoxic against various cancer cell lines and the leading complexes have remarkable cancer-cell selectivity. A detailed study of the guanidine complex 7 and the amidine complex 13 reveals two distinguished modes of action. Complex 7 weakly binds to DNA and induces DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and typical apoptosis pathways in MCF-7 cells. In contrast, complex 13 induces paraptosis-like cell death hallmarked by massive vacuole formation, mitochondrial swelling, and ER stress, resulting in significant cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells. Our results provide an extraordinary example of tuning the mechanism of action of (salen)ruthenium(iii) anticancer complexes by modifying the structure of the axial ligands.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Characterization of the Hemi-Salen Ligands and Their Triboron Complexes: Spectroscopy and Examination of Anticancer Properties.Chem Biodivers. 2018 Jan;15(1). doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201700428. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Chem Biodivers. 2018. PMID: 29032600
-
Synthesis, characterization and discovery of multiple anticancer mechanisms of dibutyltin complexes based on salen-like ligands.J Inorg Biochem. 2024 Feb;251:112434. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2023.112434. Epub 2023 Nov 24. J Inorg Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38029537
-
Imine-N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Versatile Ligands in Ruthenium(II) p-Cymene Anticancer Complexes: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study.Chem Asian J. 2018 Oct 4;13(19):2923-2933. doi: 10.1002/asia.201801058. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Chem Asian J. 2018. PMID: 30101417
-
Dimetallic Ru(II) arene complexes appended on bis-salicylaldimine induce cancer cell death and suppress invasion via p53-dependent signaling.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Sep 5;157:1480-1490. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.054. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30282320
-
Critical Overview of the Use of Ru(II) Polypyridyl Complexes as Photosensitizers in One-Photon and Two-Photon Photodynamic Therapy.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Nov 21;50(11):2727-2736. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00180. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 29058879 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complex-Cationic Peptide Hybrids Trigger Paraptosis in Cancer Cells via an Intracellular Ca2+ Overload from the Endoplasmic Reticulum and a Decrease in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential.Molecules. 2021 Nov 21;26(22):7028. doi: 10.3390/molecules26227028. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34834120 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Anthraquinone Compounds Induce Cancer Cell Death through Paraptosis.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Mar 25;10(5):732-736. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00624. eCollection 2019 May 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31097991 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiphilic Cationic Triscyclometalated Iridium(III) Complex-Peptide Hybrids Induce Paraptosis-like Cell Death of Cancer Cells via an Intracellular Ca2+-Dependent Pathway.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 17;5(12):6983-7001. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00337. eCollection 2020 Mar 31. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32258934 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel halogenated chlorido[N,N'-bis(salicylidene)-1,2-bis(3-methoxyphenyl)ethylenediamine]iron(III) complexes as anticancer agents.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024 Sep;29(6):583-599. doi: 10.1007/s00775-024-02067-9. Epub 2024 Aug 12. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39133326 Free PMC article.
-
Post-complexation Functionalization of Cyclometalated Iridium(III) Complexes and Applications to Biomedical and Material Sciences.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022 Aug 10;380(5):36. doi: 10.1007/s41061-022-00401-w. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022. PMID: 35948812 Review.
References
-
- Brabec V., Kasparkova J. Drug Resist. Updates. 2005;8:131–146. - PubMed
-
- Kelland L. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007;7:573–584. - PubMed
-
- Yan Y. K., Melchart M., Habtemariam A., Sadler P. J. Chem. Commun. 2005:4764–4776. - PubMed
-
- Bergamo A., Sava G. Dalton Trans. 2007:1267–1272. - PubMed
-
- Hartinger C. G., Jakupec M. A., Zorbas-Seifried S., Groessl M., Egger A., Berger W., Zorbas H., Dyson P. J., Keppler B. K. Chem. Biodiversity. 2008;5:2140–2155. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

