Development of Novel Polymorphic EST-SSR Markers in Bailinggu (Pleurotus tuoliensis) for Crossbreeding
- PMID: 29149037
- PMCID: PMC5704238
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8110325
Development of Novel Polymorphic EST-SSR Markers in Bailinggu (Pleurotus tuoliensis) for Crossbreeding
Abstract
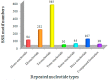
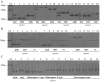
Identification of monokaryons and their mating types and discrimination of hybrid offspring are key steps for the crossbreeding of Pleurotus tuoliensis (Bailinggu). However, conventional crossbreeding methods are troublesome and time consuming. Using RNA-seq technology, we developed new expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) markers for Bailinggu to easily and rapidly identify monokaryons and their mating types, genetic diversity and hybrid offspring. We identified 1110 potential EST-based SSR loci from a newly-sequenced Bailinggu transcriptome and then randomly selected 100 EST-SSRs for further validation. Results showed that 39, 43 and 34 novel EST-SSR markers successfully identified monokaryons from their parent dikaryons, differentiated two different mating types and discriminated F₁ and F₂ hybrid offspring, respectively. Furthermore, a total of 86 alleles were detected in 37 monokaryons using 18 highly informative EST-SSRs. The observed number of alleles per locus ranged from three to seven. Cluster analysis revealed that these monokaryons have a relatively high level of genetic diversity. Transfer rates of the EST-SSRs in the monokaryons of closely-related species Pleurotuseryngii var. ferulae and Pleurotus ostreatus were 72% and 64%, respectively. Therefore, our study provides new SSR markers and an efficient method to enhance the crossbreeding of Bailinggu and closely-related species.
Keywords: Pleurotus tuoliensis; expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat; genetic diversity; monokaryon; transferability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Identified Candidate Genes Related to Bailinggu Mushroom Formation and Genetic Markers for Genetic Analyses and Breeding.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 24;7(1):9266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08049-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28839254 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis of Pleurotus eryngii subsp. tuoliensis (Bailinggu) Mycelia in Response to Cold Stimulation.Molecules. 2016 May 17;21(5):560. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050560. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27196889 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq SSRs of Moth Orchid and Screening for Molecular Markers across Genus Phalaenopsis (Orchidaceae).PLoS One. 2015 Nov 2;10(11):e0141761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141761. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26523377 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic linkage map of Pleurotus tuoliensis integrated with physical mapping of the de novo sequenced genome and the mating type loci.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 5;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4421-z. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29304732 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic relationship of two popular edible Pleurotus in China, Bailinggu (P. eryngii var. tuoliensis) and Xingbaogu (P. eryngii), determined by ITS, RPB2 and EF1α sequences.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Jun;43(6):573-82. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-3982-2. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27075657
Cited by
-
Genome Sequencing Illustrates the Genetic Basis of the Pharmacological Properties of Gloeostereum incarnatum.Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 1;10(3):188. doi: 10.3390/genes10030188. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30832255 Free PMC article.
-
Pleurotus eryngii Genomes Reveal Evolution and Adaptation to the Gobi Desert Environment.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 3;10:2024. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02024. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31551962 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analyses Provide Insights Into the Evolutionary History and Genetic Diversity of Auricularia Species.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 1;10:2255. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02255. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31632371 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a cDNA library and preliminary analysis of the expressed sequence tags of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826).Mol Med Rep. 2019 Apr;19(4):2537-2550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9938. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30720084 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient genome editing with CRISPR/Cas9 in Pleurotus ostreatus.AMB Express. 2021 Feb 20;11(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13568-021-01193-w. AMB Express. 2021. PMID: 33609205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawai G., Babasaki K., Neda H. Taxonomic position of a Chinese Pleurotus “Bai-Ling-Gu”, it belongs to Pleurotus eryngii (DC., Fr.) Quél. and evolved independently in China. Mycoscience. 2008;49:75–87. doi: 10.1007/S10267-007-0392-2. - DOI
-
- Mou C.J., Cao Y.Q., Ma J.L. A new variety of Pleurotus eryngii and its cultural characters. Acta Mycol. Sin. 1987;6:153–156.
-
- Zervakis G.I., Ntougias S., Gargano M.L., Besi M.I., Polemis E., Typas M.A., Venturella G. A reappraisal of the Pleurotus eryngii complex—New species and taxonomic combinations based on the application of a polyphasic approach, and an identification key to Pleurotus taxa associated with Apiaceae plants. Fungal Biol. 2014;118:814–834. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2014.07.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fu Y.P., Yueting Dai Y.T., Yang C.T., Wei P., Song B., Yang Y., Sun L., Zhang Z.W., Li Y. Comparative transcriptome analysis identified candidate genes related to Bailinggu mushroom formation and genetic markers for genetic analyses and breeding. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:9266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08049-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

