Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H-NMR)-Based Metabolomic Evaluation of Human Renal Allografts from Donations After Circulatory Death
- PMID: 29149095
- PMCID: PMC5702106
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.905168
Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (¹H-NMR)-Based Metabolomic Evaluation of Human Renal Allografts from Donations After Circulatory Death
Abstract
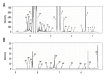
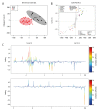
BACKGROUND Delayed graft function (DGF) is a common complication that impairs allograft function after kidney transplantation. However, the mechanism of DGF remains unclear. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based analysis has been widely used in recent times to assess changes in metabolite levels. MATERIAL AND METHODS Samples of perfusate from allografts donated after circulatory death were collected prior to transplantation, during static cold storage. ¹H-NMR-based metabolomics combined with the statistical methods, orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), and principle-component analysis (PCA), were employed to test different levels of metabolites between the allografts that exhibited DGF and those that exhibited immediate graft function (IGF). RESULTS The study population consisted of 36 subjects, 11 with DGF and 25 with IGF. Of the 37 detected and identified metabolites, a-glucose and citrate were significantly elevated in the perfusate of DGF allografts, and taurine and betaine were significantly decreased. CONCLUSIONS ¹H-NMR analysis of DGF and IGF perfusates revealed some significant differences in their metabolite profiles, which may help explain the mechanisms of kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury and DGF.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Tugmen C, Sert I, Kebabci E, et al. Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation: Risk factors and impact on early graft function. Prog Transplant. 2016;26(2):172–77. - PubMed
-
- Troppmann C, Gillingham KJ, Benedetti E, et al. Delayed graft function, acute rejection, and outcome after cadaver renal transplantation. The multivariate analysis. Transplantation. 1995;59(7):962–68. - PubMed
-
- Yarlagadda SG, Coca SG, Formica RN, Jr, et al. Association between delayed graft function and allograft and patient survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(3):1039–47. - PubMed
-
- Tahir W, Hakeem A, Dawrant M, et al. Early sirolimus conversion as rescue therapy in kidneys with prolonged delayed graft function in deceased donor renal transplant. Transplant Proc. 2015;47(6):1610–15. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig C, Ward DG, Martin A, et al. Fast targeted multidimensional NMR metabolomics of colorectal cancer. Magn Reson Chem. 2009;47(Suppl 1):S68–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

