Pearls and pitfalls in comprehensive critical care echocardiography
- PMID: 29149863
- PMCID: PMC5693549
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1866-z
Pearls and pitfalls in comprehensive critical care echocardiography
Abstract
Critical care echocardiography is developing rapidly with an increasing number of specialists now performing comprehensive studies using Doppler and other advanced techniques. However, this imaging can be challenging, interpretation is far from simple in the complex critically ill patient and mistakes can be easy to make. We aim to address clinically relevant areas where potential errors may occur and suggest methods to hopefully improve accuracy of imaging and interpretation.
Keywords: Advanced; Critical care; Doppler; Echocardiography; Intensive care.
Conflict of interest statement
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of their individual details and accompanying images (the photograph shown in Fig. 4) in this manuscript. The consent form is held by the authors and is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

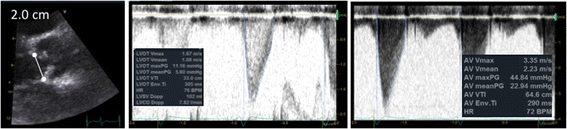
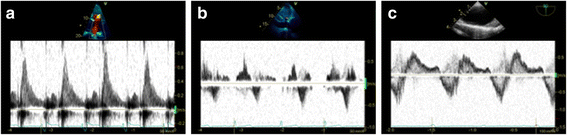
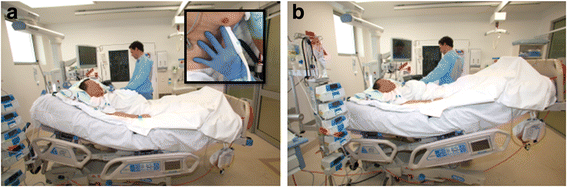


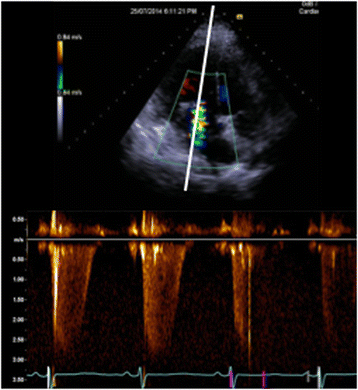
References
-
- Vieillard-Baron A, Schmitt JM, Augarde R, Fellahi JL, Prin S, Page B, et al. Acute cor pulmonale in acute respiratory distress syndrome submitted to protective ventilation: incidence, clinical implications, and prognosis. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1551–5. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200108000-00009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Quiñones MA, Otto CM, Stoddard M, Waggoner A, Zoghbi WA. Doppler quantification task force of the nomenclature and standards committee of the American society of echocardiography. Recommendations for quantification of Doppler echocardiography: a report from the Doppler quantification task force of the nomenclature and standards committee of the American society of echocardiography. JASE. 2002;15(2):167–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

