Novel insights into chromosomal conformations in cancer
- PMID: 29149895
- PMCID: PMC5693495
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0741-5
Novel insights into chromosomal conformations in cancer
Abstract
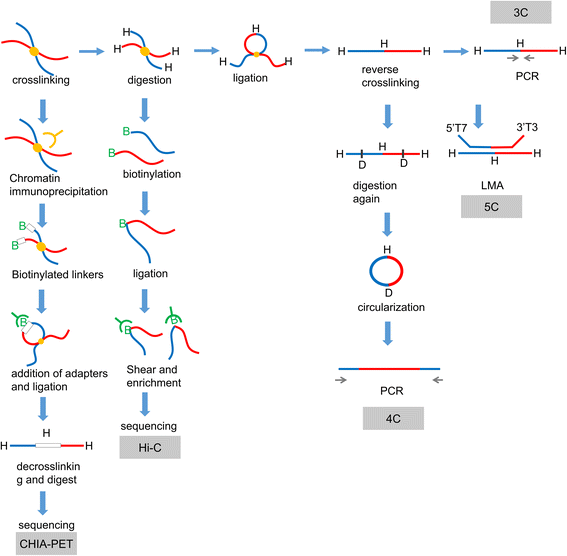
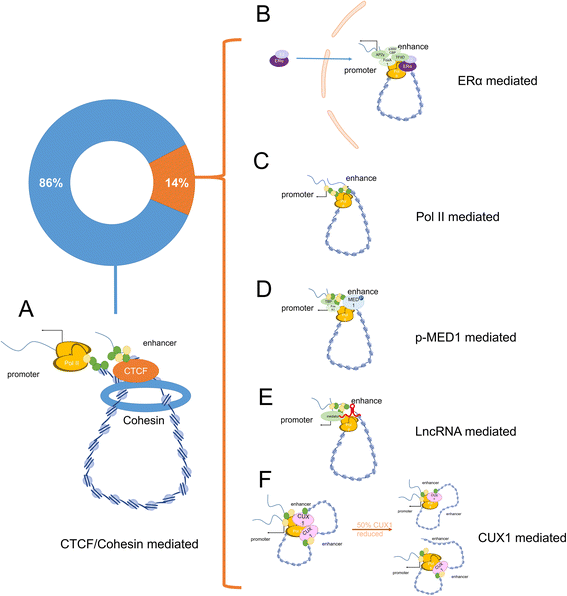
Exploring gene function is critical for understanding the complexity of life. DNA sequences and the three-dimensional organization of chromatin (chromosomal interactions) are considered enigmatic factors underlying gene function, and interactions between two distant fragments can regulate transactivation activity via mediator proteins. Thus, a series of chromosome conformation capture techniques have been developed, including chromosome conformation capture (3C), circular chromosome conformation capture (4C), chromosome conformation capture carbon copy (5C), and high-resolution chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C). The application of these techniques has expanded to various fields, but cancer remains one of the major topics. Interactions mediated by proteins or long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are typically found using 4C-sequencing and chromatin interaction analysis by paired-end tag sequencing (ChIA-PET). Currently, Hi-C is used to identify chromatin loops between cancer risk-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) found by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and their target genes. Chromosomal conformations are responsible for altered gene regulation through several typical mechanisms and contribute to the biological behavior and malignancy of different tumors, particularly prostate cancer, breast cancer and hematologic neoplasms. Moreover, different subtypes may exhibit different 3D-chromosomal conformations. Thus, C-tech can be used to help diagnose cancer subtypes and alleviate cancer progression by destroying specific chromosomal conformations. Here, we review the fundamentals and improvements in chromosome conformation capture techniques and their clinical applications in cancer to provide insight for future research.
Keywords: Cancer; Chromosomal conformations; Chromosome conformation capture; Diagnosis; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Cullen KE, Kladde MP, Seyfred MA. Interaction between transcription regulatory regions of prolactin chromatin. Science. 1993;261(5118):203–206. - PubMed
-
- Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 2002;295(5558):1306–1311. - PubMed
-
- Palstra RJ, Tolhuis B, Splinter E, Nijmeijer R, Grosveld F, de Laat W. The beta-globin nuclear compartment in development and erythroid differentiation. Nat Genet. 2003;35(2):190–194. - PubMed
-
- Tolhuis B, Palstra RJ, Splinter E, Grosveld F, de Laat W. Looping and interaction between hypersensitive sites in the active beta-globin locus. Mol Cell. 2002;10(6):1453–1465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31470757/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 17SG19/ShuGuang Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation
- 2017YQ067/Outstanding Yong Medical Scholar of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning
- 1410000159/Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at the Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning
- 2014, Class B/SMC-ChenXing Yong Scholar Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

