Dysregulation in children: Origins and implications from age 5 to age 28
- PMID: 29151386
- PMCID: PMC6460462
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579417001572
Dysregulation in children: Origins and implications from age 5 to age 28
Abstract
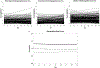
Research shows that childhood dysregulation is associated with later psychiatric disorders. It does not yet resolve discrepancies in the operationalization of dysregulation. It is also far from settled on the origins and implications of individual differences in dysregulation. This study tested several operational definitions of dysregulation using Achenbach attention, anxious/depressed, and aggression subscales. Individual growth curves of dysregulation were computed, and predictors of growth differences were considered. The study also compared the predictive utility of the dysregulation indexes to standard externalizing and internalizing indexes. Dysregulation was indexed annually for 24 years in a community sample (n = 585). Hierarchical linear models considered changes in dysregulation in relation to possible influences from parenting, family stress, child temperament, language, and peer relations. In a test of the meaning of dysregulation, it was related to functional and psychiatric outcomes in adulthood. Dysregulation predictions were further compared to those of the more standard internalizing and externalizing indexes. Growth curve analyses showed strong stability of dysregulation. Initial levels of dysregulation were predicted by temperamental resistance to control, and change in dysregulation was predicted by poor language ability and peer relations. Dysregulation and externalizing problems were associated with negative adult outcomes to a similar extent.
Figures
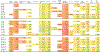
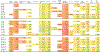
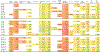
References
-
- Achenbach TM (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL (4–18), YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Achenbach TM (1998). Young Adult Self-Report for the Child Behavior Checklist. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Achenbach TM, & Rescorla L (2001). ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Aiken LS, & West SG (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

