Nomograms to Predict the Disease-free Survival and Overall Survival after Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 29151504
- PMCID: PMC5849539
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9064-17
Nomograms to Predict the Disease-free Survival and Overall Survival after Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
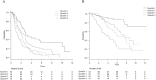
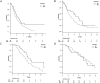
Objective The purpose of this study was to construct nomograms for the disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) of post-radiofrequency ablation (RFA) patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Furthermore, we compared the prognostic predictive ability of these nomograms for estimating per-patient outcomes with that of traditional staging systems. Methods We retrospectively enrolled 298 patients in the training set and 272 patients in the validation set who underwent RFA for HCC. The nomograms for the DFS and OS were constructed from the training set using the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model. The discriminatory accuracy of the models was compared with traditional staging systems by analyzing the Harrell's C-index. Results The DFS nomogram was developed based on the tumor size, tumor number, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), albumin, age, and α-fetoprotein. The OS nomogram was developed based on the tumor size, the model for end-stage liver disease, AST, and albumin. Our DFS and OS nomograms had good calibration and discriminatory abilities in the training set, with C-indexes of 0.640 and 0.692, respectively, that were greater than those of traditional staging systems. The C-indexes of our DFS and OS nomograms were also greater than those of traditional staging systems in the validation set, with C-indexes of 0.614 and 0.657, respectively. RFA patients were stratified into low- and high-risk groups based on the median nomogram scores. High-risk patients receiving surgical resection (SR) were associated with a better DFS and OS than those undergoing RFA. However, the DFS and OS were similar between the low-risk RFA and SR groups. Conclusion We constructed reliable and useful nomograms that accurately predict the DFS and OS after RFA for early-stage HCC patients. These graphical tools are easy to use and will assist physicians during the therapeutic decision-making process.
Keywords: disease-free survival; hepatocellular carcinoma; nomogram; overall survival; radiofrequency ablation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel nomogram to predict the local tumor progression after microwave ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A tool in prediction of successful ablation.Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):104-115. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2606. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31714685 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 29;21(1):751. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08505-0. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34187430 Free PMC article.
-
A model prediction of long-term prognosis in patients with centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing hepatectomy.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018 Oct;44(10):1595-1602. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30041973
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for breast cancer liver metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018 Nov;19(11):829-843. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1700516. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018. Retraction in: J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jun 15;23(6):528. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B17r0516. PMID: 30387333 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus resection for Barcelona clinic liver cancer very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016 Feb 23;12:295-303. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S96760. eCollection 2016. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2016. PMID: 26966370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomogram based on albumin-bilirubin grade to predict outcome of the patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after microwave ablation.Cancer Biol Med. 2019 Nov;16(4):797-810. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0486. Cancer Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31908896 Free PMC article.
-
Uni-, Bi- or Trifocal Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Western Patients: Recurrence and Survival after Percutaneous Thermal Ablation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 30;13(11):2700. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112700. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070800 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a prognostic model for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing radiofrequency ablation.Cancer Med. 2019 Sep;8(11):5023-5032. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2417. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31290618 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nomogram to predict the local tumor progression after microwave ablation in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A tool in prediction of successful ablation.Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):104-115. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2606. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31714685 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Prognostic Nomogram to Predict Progression-Free Survival of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transarterial Chemoembolization.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Jun 16;10:909-920. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S412643. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37346771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver ; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 56: 908-943, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Taura K, Ikai I, Hatano E, et al. . Influence of coexisting cirrhosis on outcomes after partial hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma fulfilling the Milan criteria: an analysis of 293 patients. Surgery 142: 685-694, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Poon RT. Optimal initial treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with preserved liver function: transplantation or resection? Ann Surg Oncol 14: 541-547, 2007. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

