Indolylalkyltriphenylphosphonium Analogues Are Membrane-Depolarizing Mycobactericidal Agents
- PMID: 29152049
- PMCID: PMC5683698
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00287
Indolylalkyltriphenylphosphonium Analogues Are Membrane-Depolarizing Mycobactericidal Agents
Abstract
Agents that selectively target the mycobacterial membrane could potentially shorten treatment time for tuberculosis, reduce relapse, and curtail emergence of resistant strains. The lipophilicity and extensive charge-delocalized state of the triphenylphosphonium cation strongly favor accumulation within bacterial membranes. Here, we explored the antimycobacterial activities and membrane-targeting properties of indolylalkyltriphenylphosphonium analogues. The most active analogues preferentially inhibited growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv (MIC50 2-4 μM) and were bactericidal against Mycobacterium bovis BCG (MBC99 3 μM). In spite of their propensity to accumulate within membranes, we found no evidence that these compounds permeabilized mycobacterial membranes or induced cell-envelope stress. Our investigations indicated that their bacterical effects stem from sustained depolarization of mycobacterial membranes and ensuing disruptive effects on electron transfer and cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
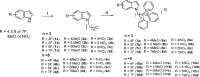


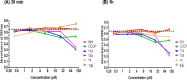
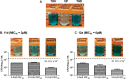
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2016; WHO Press: Paris, 2016.
-
- World Health Organization. Media Centre Fact Sheet, The Top 10 Causes of Death, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/ (accessed January 2017).
-
- World Health Organization, Media centre Fact sheet, Tuberculosis, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/ (accessed March 2017).
-
- Koh J. J.; Zou H.; Mukherjee D.; Lin S.; Lim F.; Tan J. K.; Tan D. Z.; Stocker B. L.; Timmer M. S. M.; Corkran H. M.; Lakshminarayanan R.; Tan D. T. H.; Cao D.; Beuerman R. W.; Dick T.; Liu S. Amphiphilic Xanthones as a Potent Chemical Entity of Anti-microbial Agents with Membrane-Targeting Properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 684.10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.07.068. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

