Programmed cell death 1 expression is associated with inferior survival in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma
- PMID: 29152083
- PMCID: PMC5675635
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20264
Programmed cell death 1 expression is associated with inferior survival in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma
Abstract
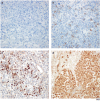
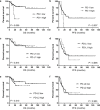
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligands PD-L1/PD-L2 have been shown to mediate immune evasion in various cancers, but their prognostic implications in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) are poorly understood. Therefore, we analyzed 76 PCNSL patients at initial diagnosis who were treated homogenously with high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy, and evaluated the prognostic roles of high immunohistochemical PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 expression. The cut-off values for high PD-1 (≥ 70 cells/high power field [HPF]), PD-L1 (≥ 100 cells/HPF), and PD-L2 (≥ 100 cells/HPF) were determined by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. Expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 was high in 7.9%, 13.2%, and 42.1% patients, respectively. High PD-1, (P = 0.007) and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) prognostic scoring (P = 0.019) were independently associated with inferior overall survival on multivariate analysis. High PD-1 also remained an independent prognostic factor for inferior progression-free survival (P = 0.028), as did MSKCC prognostic scoring (P = 0.041) on multivariate analysis. However, there were no differences in survival according to the expression levels of PD-L1/PD-L2 in PCNSL tumor microenvironment. Our results suggest that PD-1 may be considered a biomarker and potential therapeutic target in PCNSL.
Keywords: primary central nervous system lymphoma; prognosis; programmed cell death 1; programmed cell death-ligand 1; programmed cell death-ligand 2.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Association Between PD-L1 Expression and the Clinical Outcomes to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Targeted Therapy in Patients With Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Oncologist. 2015 Nov;20(11):1253-60. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0151. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26424759 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid soluble programmed death-ligand 1 is a useful prognostic biomarker in primary central nervous system lymphoma.Br J Haematol. 2023 Apr;201(1):75-85. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18598. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Br J Haematol. 2023. PMID: 36480431
-
Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Feb 13;20(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6612-2. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32054467 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoint Inhibition: Programmed Cell Death 1 and Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand Inhibitors in Hodgkin Lymphoma.Cancer J. 2016 Jan-Feb;22(1):17-22. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000164. Cancer J. 2016. PMID: 26841012 Review.
-
Programmed cell death-ligand 2: A neglected but important target in the immune response to cancer?Transl Oncol. 2020 Oct;13(10):100811. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100811. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32622310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Landscape of Immunotherapy for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 10;13(20):5061. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205061. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New hopes and challenges in targeted therapy and immunotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 18;16:1438001. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1438001. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40040699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extranodal lymphoma: pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment.Mol Biomed. 2023 Sep 18;4(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00141-3. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37718386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of pretreatment red blood cell distribution width in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system for 3P medical approaches in multiple cohorts.EPMA J. 2022 Jul 15;13(3):499-517. doi: 10.1007/s13167-022-00290-5. eCollection 2022 Sep. EPMA J. 2022. PMID: 36061828 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and clinicopathological characteristics of PD-L1 overexpression in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jan 28;20(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6550-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31992262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deckert M, Engert A, Bruck W, Ferreri AJ, Finke J, Illerhaus G, Klapper W, Korfel A, Kuppers R, Maarouf M, Montesinos-Rongen M, Paulus W, Schlegel U, Lassmann H, Wiestler OD, Siebert R, DeAngelis LM. Modern concepts in the biology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia. 2011;25:1797–1807. - PubMed
-
- Ferreri AJ, Blay JY, Reni M, Pasini F, Spina M, Ambrosetti A, Calderoni A, Rossi A, Vavassori V, Conconi A, Devizzi L, Berger F, Ponzoni M, Borisch B, Tinguely M, Cerati M, Milani M, Orvieto E, Sanchez J, Chevreau C, Dell'Oro S, Zucca E, Cavalli F. Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:266–272. - PubMed
-
- Abrey LE, Ben-Porat L, Panageas KS, Yahalom J, Berkey B, Curran W, Schultz C, Leibel S, Nelson D, Mehta M, DeAngelis LM. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5711–5715. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Girona A, Heintel D, Zhang LH, Mendy D, Gaidarova S, Brady H, Bartlett JB, Schafer PH, Schreder M, Bolomsky A, Hilgarth B, Zojer N, Gisslinger H, Ludwig H, Daniel T, Jager U, Chopra R. Lenalidomide downregulates the cell survival factor, interferon regulatory factor-4, providing a potential mechanistic link for predicting response. Br J Haematol. 2011;154:325–336. - PubMed
-
- Braaten KM, Betensky RA, de Leval L, Okada Y, Hochberg FH, Louis DN, Harris NL, Batchelor TT. BCL-6 expression predicts improved survival in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1063–1069. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

