Crystal structure of 2,4,6-tri-methyl-benzoic anhydride
- PMID: 29152362
- PMCID: PMC5683502
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017014670
Crystal structure of 2,4,6-tri-methyl-benzoic anhydride
Abstract
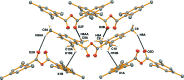
The title compound, C20H22O3, was formed in the reaction between 2,4,6-tri-methyl-benzoic acid and N,N-diiso-propyl-ethyl-amine in the presence of 1,3-di-chloro-1,3-bis-(di-methyl-amino)-propenium hydrogen dichloride, and was recrystallized from diethyl ether solution. It is the first exclusively alkyl-substituted benzoic anhydride to have been structurally characterized. The asymmetric unit consists of a half mol-ecule, the other half of which is generated by twofold rotation symmetry; the dihedral angle between the symmetry-related aromatic rings is 54.97 (3)°. The geometric parameters of the aromatic ring are typical of those for 2,4,6-tri-methyl-phenyl substituted groups. The C=O and C-O bond lengths are 1.1934 (12) and 1.3958 (11) Å, respectively, and the angle between these three atoms (O=C-O) is 121.24 (9)°. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by weak C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C-H⋯π inter-actions. The packing features wavy chains that extend parallel to [001].
Keywords: 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoic anhydride; crystal structure; mesitoic anhydride.
Figures


References
-
- Alen, G. van & Krauze, J. (1964). Z. Chem. 4, 193.
-
- Alonso, A. M., Horcajada, R., Groombridge, H. J., Mandalia, R., Motevalli, M., Utley, J. H. P. & Wyatt, P. B. (2004). Chem. Commun. pp. 412–413. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, A. M., Horcajada, R., Motevalli, M., Utley, J. H. P. & Wyatt, P. B. (2005). Org. Biomol. Chem. 3, 2842–2847. - PubMed
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Florencio, F. & Smith, P. (1970). Acta Cryst. B26, 659–666.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
