Disorders of branched chain amino acid metabolism
- PMID: 29152456
- PMCID: PMC5685199
- DOI: 10.3233/TRD-160009
Disorders of branched chain amino acid metabolism
Abstract
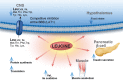
The three essential branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), leucine, isoleucine and valine, share the first enzymatic steps in their metabolic pathways, including a reversible transamination followed by an irreversible oxidative decarboxylation to coenzyme-A derivatives. The respective oxidative pathways subsequently diverge and at the final steps yield acetyl- and/or propionyl-CoA that enter the Krebs cycle. Many disorders in these pathways are diagnosed through expanded newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry. Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is the only disorder of the group that is associated with elevated body fluid levels of the BCAAs. Due to the irreversible oxidative decarboxylation step distal enzymatic blocks in the pathways do not result in the accumulation of amino acids, but rather to CoA-activated small carboxylic acids identified by gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis of urine and are therefore classified as organic acidurias. Disorders in these pathways can present with a neonatal onset severe-, or chronic intermittent- or progressive forms. Metabolic instability and increased morbidity and mortality are shared between inborn errors in the BCAA pathways, while treatment options remain limited, comprised mainly of dietary management and in some cases solid organ transplantation.
Keywords: Branched-chain; amino acid; isovaleric; maple syrup urine disease; methylmalonic; mitochondria; organic acidemia; propionic.
Figures

References
-
- Harper A.E., Miller R.H. and Block K.P., Branched-chain amino acid metabolism, Annu Rev Nutr 4 (1984), 409–454. - PubMed
-
- Chuang D.T., Wynn R.M. and Shih V.E., Maple Syrup Urine Disease (Branched-Chain Ketoaciduria, , (McGraw Hill, New York, 2008).
-
- Shimomura Y., Obayashi M., Murakami T. and Harris R.A., Regulation of branched-chain amino acid catabolism: Nutritional and hormonal regulation of activity and expression of the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase kinase, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 4 (2001), 419–423. - PubMed
-
- Hargreaves K.M. and Pardridge W.M., Neutral amino acid transport at the human blood-brain barrier, J Biol Chem 263 (1988), 19392–19397. - PubMed
-
- Kimball S.R., Shantz L.M., Horetsky R.L. and Jefferson L.S., Leucine regulates translation of specific mRNAs in L6 myoblasts through mTOR-mediated changes in availability of eIF4E and phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6, J Biol Chem 274 (1999), 11647–11652. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
