Galectin-3 and Venous Thromboembolism Incidence: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
- PMID: 29152608
- PMCID: PMC5685543
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12038
Galectin-3 and Venous Thromboembolism Incidence: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Abstract
Background: The inflammatory biomarker galectin-3 contributes to pathologic conditions such as heart failure and stimulates murine thrombogenesis. Its association with venous thromboembolism (VTE) has been sparsely studied.
Objectives: To assess the prospective association of plasma galectin-3 and the LGALS3 rs4644 SNP with VTE incidence.
Methods: We measured plasma galectin-3 in 9,916 participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study cohort in 1996 - 1998 and identified VTEs through 2013. Using Cox regression, we estimated the hazard ratio associating galectin-3 with incident VTE over a median of 13.9 years. Replication was sought in the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS).
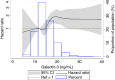
Results: ARIC included 21.8% blacks and 56.2% females with mean baseline age of 62.7 years. The incidence rate of VTE (n=389 events) increased across quintiles of galectin-3, with hazard ratios (95% CI) of 1 (reference), 1.13 (0.80 - 1.61), 1.00 (0.70 - 1.43), 1.36 (0.96 - 1.91), and 1.55 (1.09 - 2.19) (p-trend = 0.005), adjusted for age, sex, race, body mass index, diabetes status, and renal function. Results did not replicate in the CHS (124 VTE), but meta-analysis of both studies yielded a pooled hazard ratio (95% CI) for 1 SD increment in log galectin-3 of 1.10 (1.00 - 1.22). In ARIC, the C allele of rs4644 in the LGALS3 gene was associated with higher galectin-3 level, and in whites, with an increased rate of VTE.
Conclusion: Galectin-3 levels were associated positively with VTE incidence.
Keywords: Galectin-3; Gene; Prospective; Thrombosis; Venous thromboembolism.
Figures
References
-
- Wolberg AS, Rosendaal FR, Weitz JI, et al. Venous thrombosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015;1:15006. - PubMed
-
- Raskob GE, Angchaisuksiri P, Blanco AN, et al. Thrombosis: a major contributor to the global disease burden. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:1580–90. - PubMed
-
- Office of the Surgeon General . The Surgeon General's call to action to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Rockville, MD: Office of the Surgeon General; 2008. [cited 2017 Feb 1]. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK44178/. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134320/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

