The GAIT translational control system
- PMID: 29152905
- PMCID: PMC5815886
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1441
The GAIT translational control system
Abstract
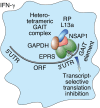
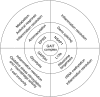
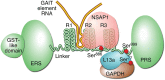
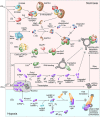
The interferon (IFN)-γ-activated inhibitor of translation (GAIT) system directs transcript-selective translational control of functionally related genes. In myeloid cells, IFN-γ induces formation of a multiprotein GAIT complex that binds structural GAIT elements in the 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs) of multiple inflammation-related mRNAs, including ceruloplasmin and VEGF-A, and represses their translation. The human GAIT complex is a heterotetramer containing glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (EPRS), NS1-associated protein 1 (NSAP1), ribosomal protein L13a (L13a), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). A network of IFN-γ-stimulated kinases regulates recruitment and assembly of GAIT complex constituents. Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5), mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), and S6K1 kinases induces EPRS release from its parental multiaminoacyl tRNA synthetase complex to join NSAP1 in a 'pre-GAIT' complex. Subsequently, the DAPK-ZIPK kinase axis phosphorylates L13a, inducing release from the 60S ribosomal subunit and binding to GAPDH. The subcomplexes join to form the functional GAIT complex. Each constituent has a distinct role in the GAIT system. EPRS binds the GAIT element in target mRNAs, NSAP1 negatively regulates mRNA binding, L13a binds eIF4G to block ribosome recruitment, and GAPDH shields L13a from proteasomal degradation. The GAIT system is susceptible to genetic and condition-specific regulation. An N-terminus EPRS truncate is a dominant-negative inhibitor ensuring a 'translational trickle' of target transcripts. Also, hypoxia and oxidatively modified lipoproteins regulate GAIT activity. Mouse models exhibiting absent or genetically modified GAIT complex constituents are beginning to elucidate the physiological role of the GAIT system, particularly in the resolution of chronic inflammation. Finally, GAIT-like systems in proto-chordates suggests an evolutionarily conserved role of the pathway in innate immunity. WIREs RNA 2018, 9:e1441. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1441 This article is categorized under: Translation > Translation Regulation RNA Interactions with Proteins and Other Molecules > RNA-Protein Complexes Regulatory RNAs/RNAi/Riboswitches > Riboswitches.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- de Nadal E, Ammerer G, Posas F. Controlling gene expression in response to stress. Nat Rev Genet 2011, 12:833–845. - PubMed
-
- Lackner DH, Bahler J. Translational control of gene expression from transcripts to transcriptomes. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2008, 271:199–251. - PubMed
-
- Dever TE. Gene‐specific regulation by general translation factors. Cell 2002, 108:545–556. - PubMed
-
- Piccirillo CA, Bjur E, Topisirovic I, Sonenberg N, Larsson O. Translational control of immune responses: from transcripts to translatomes. Nat Immunol 2014, 15:503–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

