The Wnt Inhibitor Apcdd1 Coordinates Vascular Remodeling and Barrier Maturation of Retinal Blood Vessels
- PMID: 29154126
- PMCID: PMC5728434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.025
The Wnt Inhibitor Apcdd1 Coordinates Vascular Remodeling and Barrier Maturation of Retinal Blood Vessels
Abstract
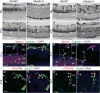
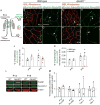
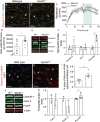
Coordinating angiogenesis with acquisition of tissue-specific properties in endothelial cells is essential for vascular function. In the retina, endothelial cells form a blood-retina barrier by virtue of tight junctions and low transcytosis. While the canonical Norrin/Fz4/Lrp5/6 pathway is essential for angiogenesis, vascular remodeling, and barrier maturation, how these diverse processes are coordinated remains poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that Apcdd1, a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, is expressed in retinal endothelial cells during angiogenesis and barrier formation. Apcdd1-deficient mice exhibit a transient increase in vessel density at ages P10-P12 due to delayed vessel pruning. Moreover, Apcdd1 mutant endothelial cells precociously form the paracellular component of the barrier. Conversely, mice that overexpress Apcdd1 in retina endothelial cells have reduced vessel density but increased paracellular barrier permeability. Apcdd1 thus serves to precisely modulate Wnt/Norrin signaling activity in the retinal endothelium and coordinate the timing of both vascular pruning and barrier maturation.
Keywords: Apcdd1; Caveolin-1; Claudin-5; Frizzled-4; Norrin; Occludin; Wnt/β-catenin signaling; angiogenesis; blood-retina barrier; tight junction; transcytosis; vascular pruning.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Adams RH, Alitalo K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:464–478. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW, Penn State Retina Research Group Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content: vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothe-lial cells. Diabetes. 1998;47:1953–1959. - PubMed
-
- Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M, Niehrs C. Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science. 2007;316:1619–1622. - PubMed
-
- Bolton SJ, Anthony DC, Perry VH. Loss of the tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occludens-1 from cerebral vascular endothelium during neutrophil-induced blood-brain barrier breakdown in vivo. Neuroscience. 1998;86:1245–1257. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

