Collective Behavior of Place and Non-place Neurons in the Hippocampal Network
- PMID: 29154129
- PMCID: PMC5720931
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.027
Collective Behavior of Place and Non-place Neurons in the Hippocampal Network
Abstract
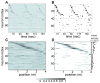
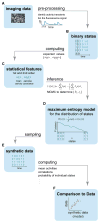
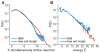
Discussions of the hippocampus often focus on place cells, but many neurons are not place cells in any given environment. Here we describe the collective activity in such mixed populations, treating place and non-place cells on the same footing. We start with optical imaging experiments on CA1 in mice as they run along a virtual linear track and use maximum entropy methods to approximate the distribution of patterns of activity in the population, matching the correlations between pairs of cells but otherwise assuming as little structure as possible. We find that these simple models accurately predict the activity of each neuron from the state of all the other neurons in the network, regardless of how well that neuron codes for position. Our results suggest that understanding the neural activity may require not only knowledge of the external variables modulating it but also of the internal network state.
Keywords: collective phenomena; hippocampus; maximum entropy; pairwise correlations; place cells.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
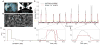



References
-
- Barbieri R, Quirk MC, Frank LM, Wilson MA, Brown EN. Construction and analysis of non-Poisson stimulus-response models of neural spiking activity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 2001;105:25–37. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia FP, Treves A. Attractor neural networks storing multiple space representations: A model for hippocampal place fields. Physical Review E. 1998;58:7738–7753.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

