Impact of chronic kidney disease on the diuretic response of tolvaptan in acute decompensated heart failure
- PMID: 29154417
- PMCID: PMC5695178
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12190
Impact of chronic kidney disease on the diuretic response of tolvaptan in acute decompensated heart failure
Abstract
Aim: This study investigated the relationship between the initial diuretic response to tolvaptan and clinical predictors for tolvaptan responders in patients with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF).
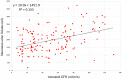
Methods and results: Patients (153) with ADHF (clinical scenario 2 or 3 with signs of fluid retention) who were administered tolvaptan were enrolled. Tolvaptan (15 or 7.5 mg) was administered for at least 7 days to those patients in whom fluid retention was observed even after standard treatment. The maximum urine volume immediately after tolvaptan administration showed good correlations with the ejection fraction and estimated glomerular filtration rate that were independent predictors of the urine volume (UV) responders (≥1500 mL increase in urine volume). The diuretic response (in terms of maximum diuresis) diminished with advancing chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage and concomitant deterioration of the renal function. Furthermore, advanced CKD was a significant negative predictor for the body weight (BW) responders (2.0% decrease in the body weight within 1 week after starting tolvaptan). As compared with non-CKD, the presence of advanced CKD predicts poor diuretic response for both UV and BW responders.
Conclusions: The diuretic response following tolvaptan administration gradually diminished with progressive deterioration of the CKD stage. Worsening renal function was not observed. Tolvaptan is effective in treating CS2 or CS3 ADHF patients who present fluid retention and congestion, suggesting its potential efficacy for fluid management in the ADHF patients with CKD without worsening the renal function.
Keywords: Acute decompensated heart failure; Chronic kidney disease; Diuretic response; Tolvaptan.
© 2017 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical benefit of tolvaptan in patients with acute decompensated heart failure and chronic kidney disease.Heart Vessels. 2016 Oct;31(10):1643-9. doi: 10.1007/s00380-015-0775-9. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 26615607
-
Early treatment with tolvaptan improves diuretic response in acute heart failure with renal dysfunction.Clin Res Cardiol. 2017 Oct;106(10):802-812. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1122-1. Epub 2017 May 24. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28540483 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of tolvaptan as a diuretic for chronic kidney disease patients.Acta Cardiol. 2015 Apr;70(2):217-23. doi: 10.1080/ac.70.2.3073514. Acta Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26148383
-
Role of vasopressin antagonists in the management of acute decompensated heart failure.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2005 Sep;2(3):131-9. doi: 10.1007/s11897-005-0021-3. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2005. PMID: 16138949 Review.
-
Urine Aquaporin-2: A Promising Marker of Response to the Arginine Vasopressin Type-2 Antagonist, Tolvaptan in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 14;17(1):105. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010105. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological interventions for heart failure in people with chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD012466. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012466.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32103487 Free PMC article.
-
Updates in heart failure: what last year brought to us.ESC Heart Fail. 2018 Dec;5(6):989-1007. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12385. ESC Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 30570225 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Decompensated Heart Failure and Renal Failure: What Is the Current Evidence?Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2018 Aug;15(4):224-238. doi: 10.1007/s11897-018-0397-5. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2018. PMID: 29987499 Review.
-
Cardiorenal syndrome: evolving concepts and pediatric knowledge gaps.Pediatr Nephrol. 2025 Mar;40(3):651-660. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06517-z. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Pediatr Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39331078 Review.
-
Effects of tolvaptan on renal function in chronic kidney disease patients with volume overload.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2018 Aug 17;11:235-240. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S167694. eCollection 2018. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30147354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg B. Acute decompensated heart failure—treatments and challenges. Circ J 2012; 76: 532–543. - PubMed
-
- Dzau VJ, Hollenberg NK, Williams GH. Neurohumoral mechanisms in heart failure: role in pathogenesis, therapy, and drug tolerance. Fed Proc 1983; 42: 3162–3169. - PubMed
-
- Gavras H. Role of vasopressin in clinical hypertension and congestive cardiac failure: interaction with the sympathetic nervous system. Clin Chem 1991; 37: 1828–1830. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith SR. Congestive heart failure: potential role of arginine vasopressin antagonists in the therapy of heart failure. Congest Heart Fail 2002; 8: 251–256. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

