Cell culture models of fatty acid overload: Problems and solutions
- PMID: 29155055
- PMCID: PMC5969525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.11.006
Cell culture models of fatty acid overload: Problems and solutions
Abstract
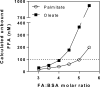
High plasma levels of fatty acids occur in a variety of metabolic diseases. Cellular effects of fatty acid overload resulting in negative cellular responses (lipotoxicity) are often studied in vitro, in an attempt to understand mechanisms involved in these diseases. Fatty acids are poorly soluble, and thus usually studied when complexed to albumins such as bovine serum albumin (BSA). The conjugation of fatty acids to albumin requires care pertaining to preparation of the solutions, effective free fatty acid concentrations, use of different fatty acid species, types of BSA, appropriate controls and ensuring cellular fatty acid uptake. This review discusses lipotoxicity models, the potential problems encountered when using these cellular models, as well as practical solutions for difficulties encountered.
Keywords: Cells and tissues; Fatty acid metabolism; Fatty acids; Lipids; Lipotoxicity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Paolisso G, Tataranni PA, Foley JE, Bogardus C, Howard BV, Ravussin E. A high concentration of fasting plasma non-esterified fatty acids is a risk factor for the development of NIDDM. Diabetologia. 1995;38:1213–1217. - PubMed
-
- Haas JT, Francque SM, Staels B. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016;78:18.1–18.25. - PubMed
-
- Hardy T, Oakley F, Anstee QM, Day CP. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and disease spectrum. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016;11:451–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

