Investigation of common, low-frequency and rare genome-wide variation in anorexia nervosa
- PMID: 29155802
- PMCID: PMC5828108
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2017.88
Investigation of common, low-frequency and rare genome-wide variation in anorexia nervosa
Erratum in
-
Correction: Investigation of common, low-frequency and rare genome-wide variation in anorexia nervosa.Mol Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;23(9):1969. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.202. Mol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30420737 Free PMC article.
Abstract
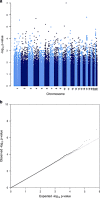
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a complex neuropsychiatric disorder presenting with dangerously low body weight, and a deep and persistent fear of gaining weight. To date, only one genome-wide significant locus associated with AN has been identified. We performed an exome-chip based genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in 2158 cases from nine populations of European origin and 15 485 ancestrally matched controls. Unlike previous studies, this GWAS also probed association in low-frequency and rare variants. Sixteen independent variants were taken forward for in silico and de novo replication (11 common and 5 rare). No findings reached genome-wide significance. Two notable common variants were identified: rs10791286, an intronic variant in OPCML (P=9.89 × 10-6), and rs7700147, an intergenic variant (P=2.93 × 10-5). No low-frequency variant associations were identified at genome-wide significance, although the study was well-powered to detect low-frequency variants with large effect sizes, suggesting that there may be no AN loci in this genomic search space with large effect sizes.
Conflict of interest statement
GB has received grant funding and consultancy fees from Eli Lilly. DD is speaker, consultant or on advisory boards of various pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, 28 Genesis Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lundbeck, Organon, Sanofi, UniPharma and Wyeth, and he has unrestricted grants from Lilly and AstraZeneca as director of the Sleep Research Unit of Eginition Hospital (National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Greece). AK is on the Shire Canada BED Advisory Board. JK is a member of SAB of AssurexHealth Inc (unpaid). ML has received lecture honoraria from Lundbeck, AstraZeneca and Biophausia Sweden, and served as scientific consultant for EPID Research Oy. There exists no other equity ownership, profit-sharing agreements, royalties, or patents. PS is scientific advisor to Pfizer, Inc. JT received an honorarium for speaking at a diabetic conference for Lilly and royalties from a published book. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Strober M, Freeman R, Lampert C, Diamond J, Kaye W. Controlled family study of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: evidence of shared liability and transmission of partial syndromes. Am J Psychiatry 2000; 157: 393–401. - PubMed
-
- Strober M, Freeman R, Lampert C, Diamond J, Kaye W. Males with anorexia nervosa: a controlled study of eating disorders in first-degree relatives. Int J Eat Disord 2001; 29: 263–269. - PubMed
-
- Lilenfeld LR, Kaye WH, Greeno CG, Merikangas KR, Plotnicov K, Pollice C et al. A controlled family study of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: psychiatric disorders in first-degree relatives and effects of proband comorbidity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998; 55: 603–610. - PubMed
-
- Bulik CM, Slof-Op’t Landt MCT, van Furth EF, Sullivan PF. The genetics of anorexia nervosa. Annu Rev Nutr 2007; 27: 263–275. - PubMed
-
- Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Tozzi F, Furberg H, Lichtenstein P, Pedersen NL. Prevalence, heritability, and prospective risk factors for anorexia nervosa. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006; 63: 305–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA133996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097007/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J500355/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT088827/Z/09/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109528/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH109782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011740/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA093459/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

