Lack of Antidepressant Effects of (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine in a Rat Learned Helplessness Model: Comparison with (R)-Ketamine
- PMID: 29155993
- PMCID: PMC5795355
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx108
Lack of Antidepressant Effects of (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine in a Rat Learned Helplessness Model: Comparison with (R)-Ketamine
Abstract
Background: (R)-Ketamine exhibits rapid and sustained antidepressant effects in animal models of depression. It is stereoselectively metabolized to (R)-norketamine and subsequently to (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine in the liver. The metabolism of ketamine to hydroxynorketamine was recently demonstrated to be essential for ketamine's antidepressant actions. However, no study has compared the antidepressant effects of these 3 compounds in animal models of depression.
Methods: The effects of a single i.p. injection of (R)-ketamine, (R)-norketamine, and (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine in a rat learned helplessness model were examined.
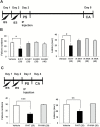
Results: A single dose of (R)-ketamine (20 mg/kg) showed an antidepressant effect in the rat learned helplessness model. In contrast, neither (R)-norketamine (20 mg/kg) nor (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine (20 and 40 mg/kg) did so.
Conclusions: Unlike (R)-ketamine, its metabolite (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine did not show antidepressant actions in the rat learned helplessness model. Therefore, it is unlikely that the metabolism of ketamine to hydroxynorketamine is essential for ketamine's antidepressant actions.
Keywords: (R)-ketamine; (R)-norketamine (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine; learned helplessness; metabolism.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is Metabolism of (R)-Ketamine Essential for the Antidepressant Effects?Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Feb 1;21(2):154-156. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx120. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29294032 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Domino EF.(2010)Taming the ketamine tiger. 1965. Anesthesiology 113:678–684 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

