SHYCD induces APE1/Ref-1 subcellular localization to regulate the p53-apoptosis signaling pathway in the prevention and treatment of acute on chronic liver failure
- PMID: 29156683
- PMCID: PMC5689573
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19891
SHYCD induces APE1/Ref-1 subcellular localization to regulate the p53-apoptosis signaling pathway in the prevention and treatment of acute on chronic liver failure
Abstract
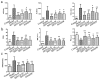
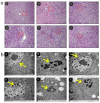
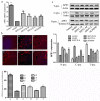
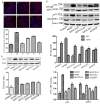
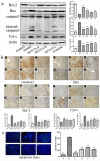
Background & Aims: San huang yin chi decoction(SHYCD) is derived from the yin chen hao decoction, a well-known and canonical Chinese medicine formula from the "Treatise on Febrile Diseases". Over the past decade, SHYCD has been used to treat and prevent the liver cirrhosis and liver failure. In the present study, we investigated the effects of SHYCD for acute on chronic liver failure(ACLF) and explored its potential mechanism. an ACLF rat model, which induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) combined with D-galactosamine (D-GalN) and lipopolysaccharide(LPS), was used and confirmed by B-ultrasound analysis. Rats were randomly divided into control group, model group, SHYCD-H group, SHYCD-M group, SHYCD-L group, AGNHW group. Compared with the ACLF model group, High, medium, and low doses of SHYCD reduced ALT, AST, TBIL, NH3, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα expression levels in the serum, Shorten PT and INR time,and increased Fbg content in the whole blood, increased survival rate of the rats, improved liver pathological changes. APE1 / Ref-1 was mainly expressed in the nucleus, but the nucleus and cytoplasm were co-expressed after hepatocyte injury. SHYCD significantly downregulated APE1/Ref-1 expression in the cytoplasm. Increased APE1/Ref-1, Bcl-2, reduced p53, caspase-3, Bax, and Cyt-c in the total protein. Base on the results, we conclused that High, medium, and low doses of SHYCD could be applied in prevention and treatment of ACLF, and dose-dependent. The possible mechanism is to promote the APE1 / Ref-1 from the cytoplasm to the nuclear transfer, regulation of p53 apoptosis signal pathway prevention and treatment of ACLF.
Keywords: APE1/Ref-1; Pathology Section; San huang yin chi decoction; acute on chronic liver failure; apoptosis; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors are solely responsible for the statements made herein.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Sanhuangyinchi decoction pretreatment ameliorates acute hepatic failure in rats by suppressing antioxidant stress and caspase-3 expression].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Apr;34(4):482-6. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 24752092 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Sanhuangyinchi decoction on liver damage and caspase-3 in rats with acute hepatic failure].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Nov;30(11):2443-5. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21097400 Chinese.
-
[Prevention and treatment mechanism of qingxia therapy (based on yinchenhao decoction and dachengqi decoction) on hepatocyte apoptosis in rats with acute hepatic injury induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine].Zhong Yao Cai. 2014 May;37(5):848-52. Zhong Yao Cai. 2014. PMID: 25335295 Chinese.
-
The intracellular localization of APE1/Ref-1: more than a passive phenomenon?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005 Mar-Apr;7(3-4):367-84. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.367. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005. PMID: 15706084 Review.
-
New Horizons for the Roles and Association of APE1/Ref-1 and ABCA1 in Atherosclerosis.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Oct 14;14:5251-5271. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S330147. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34703267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The progress to establish optimal animal models for the study of acute-on-chronic liver failure.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 9;10:1087274. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1087274. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36844207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospect of Animal Models for Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure: A Mini-review.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022 Oct 28;10(5):995-1003. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00086. Epub 2022 Apr 28. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36304511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Lianhua Qingwen on Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury: A Network Pharmacology Approach.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 14;12:717652. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.717652. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34721017 Free PMC article.
-
HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway.Open Life Sci. 2024 Jul 24;19(1):20220919. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0919. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071496 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting subcellular localization of multisite proteins using differently weighted multi-label k-nearest neighbors sets.Technol Health Care. 2019;27(S1):185-193. doi: 10.3233/THC-199018. Technol Health Care. 2019. PMID: 31045538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willars C. Update in intensive care medicine: acute liver failure. Initial management, supportive treatment and who to transplant. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2014;20:202–09. - PubMed
-
- Hu X, Zhang Y, Chen G, Li Y, Zhong S. Distribution of traditional Chinese medicine patterns in 324 cases with hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: a prospective, cross-sectional survey. J Tradit Chin Med. 2012;32:538–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

