MiR-2964a-5p binding site SNP regulates ATM expression contributing to age-related cataract risk
- PMID: 29156695
- PMCID: PMC5689585
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17600
MiR-2964a-5p binding site SNP regulates ATM expression contributing to age-related cataract risk
Abstract
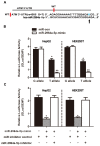
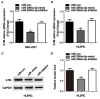
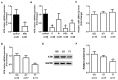
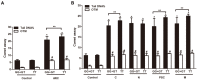
This study was to explore the involvement of DNA repair genes in the pathogenesis of age-related cataract (ARC). We genotyped nine single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of genes responsible to DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) in 804 ARC cases and 804 controls in a cohort of eye diseases in Chinese population and found that the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene-rs4585:G>T was significantly associated with ARC risk. An in vitro functional test found that miR-2964a-5p specifically down-regulated luciferase reporter expression and ATM expression in the cell lines transfected with rs4585 T allele compared to rs4585 G allele. The molecular assay on human tissue samples discovered that ATM expression was down-regulated in majority of ARC tissues and correlated with ATM genotypes. In addition, the Comet assay of cellular DNA damage of peripheral lymphocytes indicated that individuals carrying the G allele (GG/GT) of ATM-rs4585 had lower DNA breaks compared to individuals with TT genotype. These findings suggested that the SNP rs4585 in ATM might affect ARC risk through modulating the regulatory affinity of miR-2964a-5p. The reduced DSBs repair might be involved in ARC pathogenesis.
Keywords: DNA damage; age-related cataract; ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) gene; microRNA; single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Klein BE, Klein R, Linton KL. Prevalence of age-related lens opacities in a population. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1992;99:546–52. - PubMed
-
- Asbell PA, Dualan I, Mindel J, Brocks D, Ahmad M, Epstein S. Age-related cataract. Lancet. 2005;365:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Su S, Yao Y, Zhu R, Liang C, Jiang S, Hu N, Zhou J, Yang M, Xing Q, Guan H. The associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms of DNA repair genes, DNA damage, and age-related cataract: Jiangsu Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54:1201–07. - PubMed
-
- Liu XC, Liu XF, Hu ZD, Li ZH. Polymorphisms of DNA repair genes XPD (Lys751Gln) and XRCC1 (Arg399Gln), and the risk of age-related cataract: a meta-analysis. Curr Eye Res. 2015;40:676–82. - PubMed
-
- Lees-Miller SP, Meek K. Repair of DNA double strand breaks by non-homologous end joining. Biochimie. 2003;85:1161–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

