Interleukin-31 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in plasma and lymph node from Hodgkin lymphoma patients
- PMID: 29156718
- PMCID: PMC5689608
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19665
Interleukin-31 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression in plasma and lymph node from Hodgkin lymphoma patients
Abstract
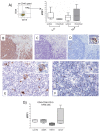
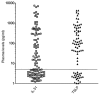
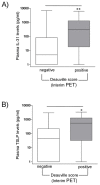
Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL) is a tumor of B-cell origin characterized by Hodgkin and Reed-Stenberg (H/RS) cells embedded in an inflammatory tissue where numerous cytokines/chemokines contribute to shape the microenvironment, leading to the typical clinical symptoms. We investigated: i) the expression of Interleukin-IL-31 (IL-31) and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP), two Th2-related cytokines with tumor-promoting and pruritogenic functions, and of the respective receptors in HL invaded lymph nodes by flow cytometry, and ii) the potential association of IL-31/TSLP plasma concentrations with clinical characteristics by ELISA. H/RS cells and the major immune cell types infiltrating HL lymph nodes expressed intracytoplasmic and surface IL-31/TSLP, and their receptors. A subgroup of patients showing at diagnosis elevated IL-31 and TSLP plasma levels had an International Prognostic Score>2, indicative of high risk of relapse, and a subsequent positive interim PET-scan, indicative of insufficient response to chemotherapy. No correlation was found between IL-31/TSLP plasma levels and overall or event-free survival. In conclusion, IL-31/TSLP and their receptors are expressed in HL cells and in immune cells infiltrating affected lymph nodes, where both cytokines may contribute to local immune suppression. The clinical impact of IL-31 and TSLP plasma levels has to be further defined in larger patient cohorts.
Keywords: Hodgkin lymphoma; IL-31; PET; TSLP; cytokine receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures

References
-
- Aldinucci D, Gloghini A, Pinto A, De Filippi R, Carbone A. The classical Hodgkin's lymphoma microenvironment and its role in promoting tumour growth and immune escape. J Pathol. 2010;221:248–263. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Sattarzadeh A, Diepstra A, Visser L, van den Berg A. The microenvironment in classical Hodgkin lymphoma: an actively shaped and essential tumor component. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;24:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Marafioti T, Hummel M, Foss HD, Laumen H, Korbjuhn P, Anagnostopoulos I, Lammert H, Demel G, Theil J, Wirth T, Stein H. Hodgkin and reed-sternberg cells represent an expansion of a single clone originating from a germinal center B-cell with functional immunoglobulin gene rearrangements but defective immunoglobulin transcription. Blood. 2000;95:1443–1450. - PubMed
-
- Re D, Kuppers R, Diehl V. Molecular pathogenesis of Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:6379–6386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

