SCO-spondin oligopeptide inhibits angiogenesis in glioblastoma
- PMID: 29156770
- PMCID: PMC5689660
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20837
SCO-spondin oligopeptide inhibits angiogenesis in glioblastoma
Abstract
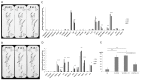
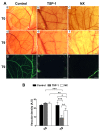
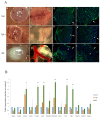
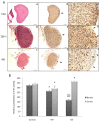
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in glioblastoma growth and progression. We therefore aimed at evaluating the anti-angiogenic properties of an oligopeptide originating from SCO-spondin (NX) on a model of human glioblastoma. To this end, we studied the impact of NX treatment on human brain endothelial cells (HBMECs) alone or co-cultured with glioblastoma cells (U87-MG) on apoptosis, proliferation, migration and release of angiogenic factors. We further investigated the anti-angiogenic potential of NX on human glioblastoma cells grown on chorio-allantoic membrane (CAM) or in glioblastoma xenografts. The results of our experiments showed that NX treatment impaired the microvascular network and induced a decrease in cell proliferation, vascularization and tumor growth in the CAM model as well as in xenotransplants. Interestingly, our in vitro experiments showed that NX impairs HBMECs migration but also regulates the release of angiogenic factors from U87-MG. These results are confirmed by the profiling of NX-treated U87-MG grown on CAM that highlighted modifications of several genes involved in angiogenesis. In conclusion, NX inhibits tumorigenesis by impairing the ability of glioblastoma cells to induce angiogenesis and by inhibiting endothelial cell migration. This molecule might therefore be an interesting candidate for future cancer therapies.
Keywords: NX peptide; SCO-spondin; TSR; glioblastoma; tumor angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No conflicts of interests was disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Nabors LB, Fiveash J. Treatment of adults with recurrent malignant glioma. Expert Rev Neurother. 2005;5:509–14. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.5.4.509. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yap R, Veliceasa D, Emmenegger U, Kerbel RS, McKay LM, Henkin J, Volpert OV. Metronomic Low-Dose Chemotherapy Boosts CD95-Dependent Antiangiogenic Effect of the Thrombospondin Peptide ABT-510: A Complementation Antiangiogenic Strategy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6678–85. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0621. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yee KO, Streit M, Hawighorst T, Detmar M, Lawler J. Expression of the Type-1 Repeats of Thrombospondin-1 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Activation of Transforming Growth Factor-β. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:541–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63319-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iruela-Arispe ML, Lombardo M, Krutzsch HC, Lawler J, Roberts DD. Inhibition of Angiogenesis by Thrombospondin-1 Is Mediated by 2 Independent Regions Within the Type 1 Repeats. Circulation. 1999;100:1423–31. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.100.13.1423. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nabors LB, Fiveash JB, Markert JM, Kekan MS, Gillespie GY, Huang Z, Johnson MJ, Meleth S, Kuo H, Gladson CL, Fathallah-Shaykh HM. A phase 1 trial of ABT-510 concurrent with standard chemoradiation for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Arch Neurol. 2010;67:313–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2010.16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

