Protective effect of Ginkgo biloba leaves extract, EGb761, on myocardium injury in ischemia reperfusion rats via regulation of TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 29156826
- PMCID: PMC5689716
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21372
Protective effect of Ginkgo biloba leaves extract, EGb761, on myocardium injury in ischemia reperfusion rats via regulation of TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
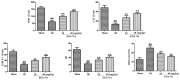
Beneficial actions of EGb 761 against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in lung, brain and renal ischemia have been described. However, the relationship between EGb 761 and signal molecules in myocardial ischemia reperfusion has not been well elucidated. In this study, we investigated the effects and mechanism of EGb 761 preconditioning on anti-myocardial I/R injuries in vivo. Meanwhile, their potential anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation effect were assessed. Hemodynamic parameters were monitored as left ventricular systolic pressure, LV end-diastolic pressure and maximal rate of increase and decrease of left ventricular pressure (dP/dtmax). The oxidative stress indicators and inflammatory factors were also evaluated. Western blot method was used for analysis of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), p-TLR4, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), p-NF-κB p65, Bax and Bcl-2 protein expressions. EGb 761 significantly improved cardiac function, decreased levels of creatine kinase, aspartate aminotransferase and lactate dehydrogenase. EGb 761 also restrained the oxidative stress related to myocardial ischemia injury as evidenced by decreased malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione-peroxidase, glutathione reductase activity. Meanwhile, the inflammatory cascade was inhibited as evidenced by decreased cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6 and interleukin-1β. Our results still showed that EGb 761 pretreatment significantly decrease the level of cleaved Bax, and increase the level of Bcl-2 in rats subjected to I/R injury. Simultaneously, the expressions of myocardial TLR4 and NF-κB were significantly decreased. It can be concluded that EGb 761 pretreatment was protected against myocardium I/R injury by decreasing oxidative stress, repressing inflammatory cascade in vivo and inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway.
Keywords: EGb761; TLR-4/NF-κB pathway; myocardial ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors declare that they have not any conflicts of interest.
Figures




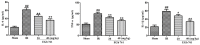



References
-
- Zweier JL, Talukder MA. The role of oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70:181–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.02.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roth E, Lantos J, Temes G, Varga G, Paroczai M, Karpati E. Cardioprotection during heart ischemia-reperfusion. Acta Chir Hung. 1997;36:306–9. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Fu W, Yuan W, Wu Z, Yang Z. A study of time window for oxidative stress associated with myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Chin Med J (Engl) 1996;109:926–9. - PubMed
-
- Thompson-Gorman SL, Zweier JL. Evaluation of the role of xanthine oxidase in myocardial reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:6656–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

