Imbalanced plasma ACE and ACE2 level in the uremic patients with cardiovascular diseases and its change during a single hemodialysis session
- PMID: 29157100
- PMCID: PMC6446170
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1398665
Imbalanced plasma ACE and ACE2 level in the uremic patients with cardiovascular diseases and its change during a single hemodialysis session
Abstract
Background: The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has significant influences on heart and renal disease progression. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) and angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2) are major peptidases of RAS components and play counteracting functions through angiotensin II (Ang II)/ATIR and angiotensin-(1-7) (Ang-(1-7))/Mas axis, respectively.
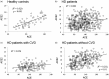
Methods: There were 360 uremic patients on regular hemodialysis (HD) treatment (inclusive of 119 HD patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and 241 HD patients without CVD and 50 healthy subjects were enrolled in this study. Plasma ACE, ACE2, Ang II and Ang-(1-7) levels of the HD patients were determined.
Results: We compared pre-HD levels of plasma ACE, ACE2, Ang II and Ang-(1-7) in the HD patients with and without CVD to those of the controls. The HD patients, particularly those with CVD, showed a significant increase in the levels of ACE and Ang II, whereas ACE2 and Ang-(1-7) levels were lower than those in the healthy controls. Therefore, imbalanced ACE/ACE2 was observed in the HD patients with CVD. In the course of a single HD session, the plasma ACE, ACE/ACE2 and Ang II levels in the HD patients with CVD were increased from pre-HD to post-HD. On the contrary, ACE2 levels were decreased after the HD session. These changes were not detected in the HD patients without CVD.
Conclusions: Pathogenically imbalanced circulating ACE/ACE2 was detected in the HD patients, particularly those with CVD. HD session could increase ACE/Ang II/AT1R axis and decrease ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis activity in the circulation of HD patients with CVD.
Keywords: Angiotensin converting enzyme; angiotensin converting enzyme II; cardiovascular diseases; hemodialysis; renin-angiotensin system; uremic patient.
Figures
References
-
- Santos RA, Ferreira AJ, Verano-Braga T, et al. . Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, angiotensin-(1–7) and Mas: new players of the renin-angiotensin system. J Endocrinol. 2013;216:R1–R17. - PubMed
-
- Burns KD.The emerging role of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 in the kidney. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2007;16:116–121. - PubMed
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, et al. . A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33238–33243. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al. . A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
