Brain medical image diagnosis based on corners with importance-values
- PMID: 29157218
- PMCID: PMC5697385
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-017-1903-6
Brain medical image diagnosis based on corners with importance-values
Abstract
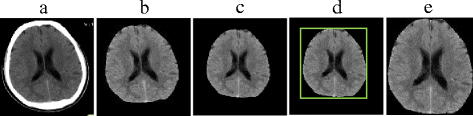
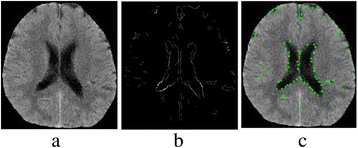
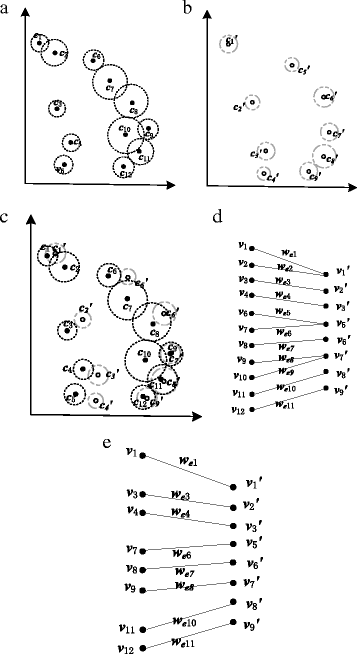
Background: Brain disorders are one of the top causes of human death. Generally, neurologists analyze brain medical images for diagnosis. In the image analysis field, corners are one of the most important features, which makes corner detection and matching studies essential. However, existing corner detection studies do not consider the domain information of brain. This leads to many useless corners and the loss of significant information. Regarding corner matching, the uncertainty and structure of brain are not employed in existing methods. Moreover, most corner matching studies are used for 3D image registration. They are inapplicable for 2D brain image diagnosis because of the different mechanisms. To address these problems, we propose a novel corner-based brain medical image classification method. Specifically, we automatically extract multilayer texture images (MTIs) which embody diagnostic information from neurologists. Moreover, we present a corner matching method utilizing the uncertainty and structure of brain medical images and a bipartite graph model. Finally, we propose a similarity calculation method for diagnosis.
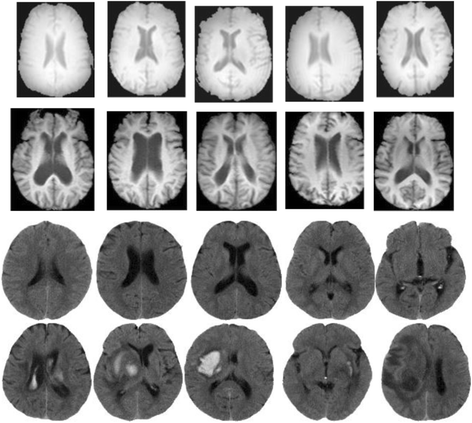
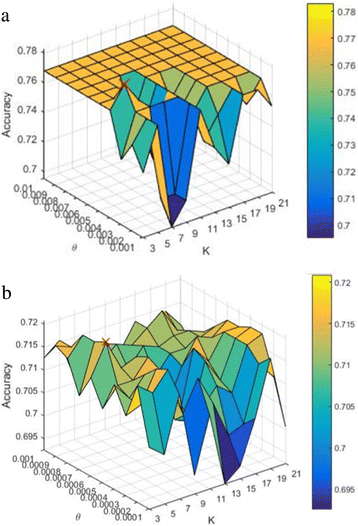
Results: Brain CT and MRI image sets are utilized to evaluate the proposed method. First, classifiers are trained in N-fold cross-validation analysis to produce the best θ and K. Then independent brain image sets are tested to evaluate the classifiers. Moreover, the classifiers are also compared with advanced brain image classification studies. For the brain CT image set, the proposed classifier outperforms the comparison methods by at least 8% on accuracy and 2.4% on F1-score. Regarding the brain MRI image set, the proposed classifier is superior to the comparison methods by more than 7.3% on accuracy and 4.9% on F1-score. Results also demonstrate that the proposed method is robust to different intensity ranges of brain medical image.
Conclusions: In this study, we develop a robust corner-based brain medical image classifier. Specifically, we propose a corner detection method utilizing the diagnostic information from neurologists and a corner matching method based on the uncertainty and structure of brain medical images. Additionally, we present a similarity calculation method for brain image classification. Experimental results on two brain image sets show the proposed corner-based brain medical image classifier outperforms the state-of-the-art studies.
Keywords: Bipartite graph; Brain medical image diagnosis; Classification; Corner detection; Corner matching; Multilayer texture images.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
For Dmri, ethics approval is not required as the human data were publicly available by ADNI website, and all the data are not identifiable. For Dct, informed consent was obtained in accordance with institutional policies in use in each country.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spatial-aware contrastive learning for cross-domain medical image registration.Med Phys. 2024 Nov;51(11):8141-8150. doi: 10.1002/mp.17311. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39031488
-
Segmentation of perivascular spaces in 7T MR image using auto-context model with orientation-normalized features.Neuroimage. 2016 Jul 1;134:223-235. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.03.076. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 27046107 Free PMC article.
-
3D cerebral MR image segmentation using multiple-classifier system.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017 Mar;55(3):353-364. doi: 10.1007/s11517-016-1483-z. Epub 2016 May 20. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017. PMID: 27207464
-
Validation of the Gatortail method for accurate sizing of pulmonary vessels from 3D medical images.Med Phys. 2017 Dec;44(12):6314-6328. doi: 10.1002/mp.12580. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28905390
-
Revolution at the Corner Drugstore.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2016 Apr;7(3):258-260. doi: 10.6004/jadpro.2016.7.3.2. Epub 2016 Apr 1. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2016. PMID: 29152385 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Supplements Significantly Improve the Growth Rate of Cultured Asparagopsis armata.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025 Mar 14;27(2):65. doi: 10.1007/s10126-025-10440-1. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40085266 Free PMC article.
-
MADGAN: unsupervised medical anomaly detection GAN using multiple adjacent brain MRI slice reconstruction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Apr 26;22(Suppl 2):31. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03936-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33902457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jing Sh R, Hai WP, Peng YL, et al. Symmetry theory based classification algorithm in brain computed tomography image database. J Med Imaging Health Inform. 2016;6(1):22–33. doi: 10.1166/jmihi.2016.1596. - DOI
-
- Ding, Yi, et al. "Classification of Alzheimer's disease based on the combination of morphometric feature and texture feature."Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), 2015 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2015.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

