Identification of immunogenic proteins of the cysticercoid of Hymenolepis diminuta
- PMID: 29157281
- PMCID: PMC5697066
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2519-4
Identification of immunogenic proteins of the cysticercoid of Hymenolepis diminuta
Abstract
Background: A wide range of molecules are used by tapeworm metacestodes to establish successful infection in the hostile environment of the host. Reports indicating the proteins in the cestode-host interactions are limited predominantly to taeniids, with no previous data available for non-taeniid species. A non-taeniid, Hymenolepis diminuta, represents one of the most important model species in cestode biology and exhibits an exceptional developmental plasticity in its life-cycle, which involves two phylogenetically distant hosts, arthropod and vertebrate.
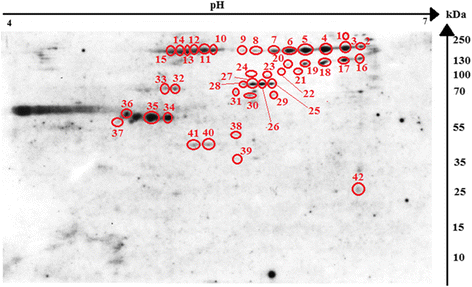
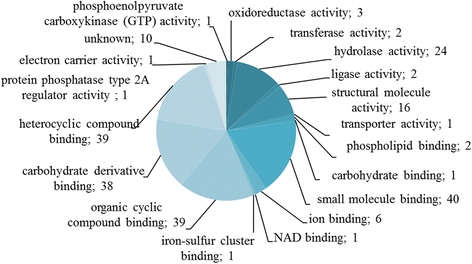
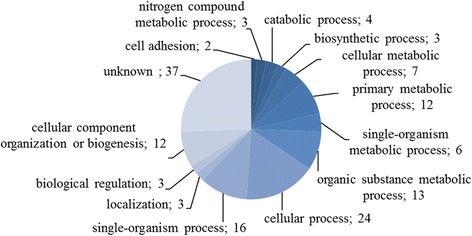
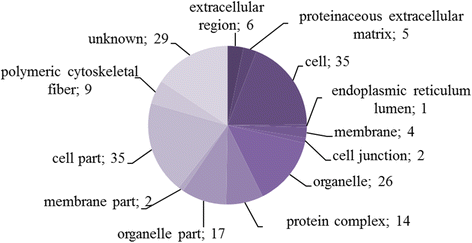
Results: We identified H. diminuta cysticercoid proteins that were recognized by sera of H. diminuta-infected rats using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE), 2D-immunoblotting, and LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry. Proteomic analysis of 42 antigenic spots revealed 70 proteins. The largest number belonged to structural proteins and to the heat-shock protein (HSP) family. These results show a number of the antigenic proteins of the cysticercoid stage, which were present already in the insect host prior to contact with the mammal host. These are the first parasite antigens that the mammal host encounters after the infection, therefore they may represent some of the molecules important in host-parasite interactions at the early stage of infection.
Conclusions: These results could help in understanding how H. diminuta and other cestodes adapt to their diverse and complex parasitic life-cycles and show universal molecules used among diverse groups of cestodes to escape the host response to infection.
Keywords: Hymenolepis diminuta; Immunogenic proteins; Mass spectrometry; Two-dimensional electrophoresis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures used in the present study had been pre-approved by the 3rd Local Ethical Committee for Scientific Experiments on Animals in Warsaw, Poland (resolution No. 51/2012, 30th of May 2012).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Hymenolepis diminuta Cysticercoid and Adult Stages.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jan 15;8:2672. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02672. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29379475 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoproteomics and Surfaceomics of the Adult Tapeworm Hymenolepis diminuta.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 12;9:2487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02487. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30483248 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry analysis of the excretory-secretory (E-S) products of the model cestode Hymenolepis diminut a reveals their immunogenic properties and the presence of new E-S proteins in cestodes.Acta Parasitol. 2016 Mar;61(2):429-42. doi: 10.1515/ap-2016-0058. Acta Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27078671
-
Hymenolepis diminuta infections in tenebrionid beetles as a model system for ecological interactions between helminth parasites and terrestrial intermediate hosts: a review and meta-analysis.J Parasitol. 2014 Feb;100(1):46-58. doi: 10.1645/13-347.1. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 23952690 Review.
-
Selected Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Parasite⁻Host System Hymenolepis diminuta⁻Rattus norvegicus.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 17;19(8):2435. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082435. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30126154 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoproteomic Analysis of Dirofilaria repens Microfilariae and Adult Parasite Stages.Pathogens. 2021 Feb 5;10(2):174. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020174. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33562513 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Hymenolepis diminuta Cysticercoid and Adult Stages.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jan 15;8:2672. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02672. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29379475 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression, purification, and kinetic characterization of mitochondrial thioredoxin (TsTrx2), cytosolic thioredoxin (TsTrx1), and glutaredoxin (TsGrx1) from Taenia solium.Parasitol Res. 2019 Jun;118(6):1785-1797. doi: 10.1007/s00436-019-06336-4. Epub 2019 May 6. Parasitol Res. 2019. PMID: 31062084
-
What about the Cytoskeletal and Related Proteins of Tapeworms in the Host's Immune Response? An Integrative Overview.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 18;12(6):840. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12060840. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37375530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fasciola hepatica Extracellular Vesicles isolated from excretory-secretory products using a gravity flow method modulate dendritic cell phenotype and activity.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Sep 8;14(9):e0008626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008626. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32898175 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

