Smoldering myocarditis following immune checkpoint blockade
- PMID: 29157297
- PMCID: PMC5697345
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-017-0296-4
Smoldering myocarditis following immune checkpoint blockade
Abstract
Background: Severe myocarditis associated with electrical conduction abnormalities and occasionally heart failure has been well documented following treatment with immune checkpoint blockade with an estimated incidence of less than 1%. However, the incidence, early detection, and management of less severe immune-related myocarditis are unknown since most immunotherapy trials have not included routine cardiac monitoring. Herein, we provide the first description of subclinical or smoldering myocarditis with minimal signs and symptoms following immune checkpoint blockade with a single dose of ipilimumab and nivolumab.
Case presentation: Our patient was diagnosed with immune checkpoint blockade-induced myocarditis based upon an acute rise in serum cardiac troponin I beginning 2 weeks after the initial dose of ipilimumab/nivolumab consistent with the reported median onset of clinical myocarditis at 17 days, as well as a lack of other causes despite extensive cardiac evaluation. The patient initially presented with intractable nausea with no known gastrointestinal etiology. High dose glucocorticoid therapy led to rapid resolution of nausea and a four-fold decrease in troponin I over 4 days. Serum troponin I spiked again following a steroid taper to 13 times the upper limit of normal with endomyocardial biopsy revealing collagen fibrosis and lymphocytic inflammation predominantly comprised of CD8+ T cells consistent with chronic smoldering myocarditis. Serum anti-striated muscle antibodies were also detected with no evidence of rhabdomyolysis. Serum cardiac troponin I levels as an indicator of ongoing myocyte damage gradually improved with chronic prednisone at 10 mg daily. Late addition of intravenous immunoglobulin was associated with rapid normalization of creatine kinase-myocardial band.
Conclusions: This case demonstrates that subclinical, smoldering myocarditis may occur following immune checkpoint blockade, with evidence of both humoral and cell-mediated immunity responsive to corticosteroid therapy. This experience supports early monitoring for myocarditis with serial electrocardiograms and serum troponin I determinations in large, prospective cohorts of patients receiving combination immune checkpoint blockade as early detection and initiation of immunosuppression may forestall fulminant presentation of this disease and limit myocardial damage.
Keywords: Antibody; Cardio-oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Immune checkpoint blockade; Ipilimumab; Melanoma; Myocarditis; Nivolumab; Troponin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient/participant (delete as appropriate) for publication of their individual details and accompanying images in this manuscript. The consent form is held by the authors/by the authors’ institution/in the patients’ clinical notes (delete as appropriate) and is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief.
Competing interests
DBJ serves on advisory boards for BMS, Genoptix, Incyte, and Merck. RMC serves on speaker bureaus for BMS, Merck, Novartis, and Genentech. The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
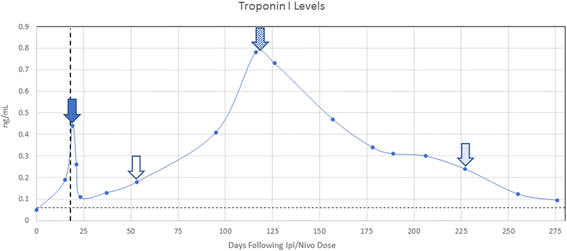
 , end of steroid taper
, end of steroid taper  , initiation of prednisone at 10 mg daily,
, initiation of prednisone at 10 mg daily,  and initiation of intravenous immunoglobulin
and initiation of intravenous immunoglobulin  . Vertical dashed line represents the previously reported median onset of clinical myocarditis at 17 days following immune CPB. Horizontal dashed line represents the upper limit of normal for serum cTnI at 0.06 ng/mL
. Vertical dashed line represents the previously reported median onset of clinical myocarditis at 17 days following immune CPB. Horizontal dashed line represents the upper limit of normal for serum cTnI at 0.06 ng/mL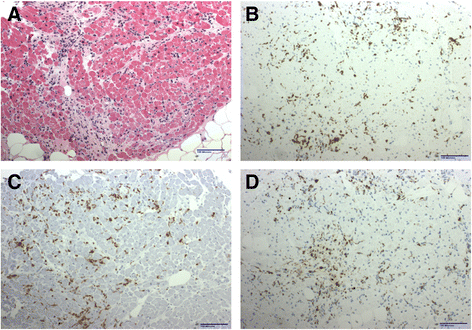
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
