Sleep in children with type 1 diabetes and their parents in the T1D Exchange
- PMID: 29157581
- PMCID: PMC7650845
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sleep.2017.07.005
Sleep in children with type 1 diabetes and their parents in the T1D Exchange
Abstract
Objectives: Sleep has physiological and behavioral impacts on diabetes outcomes, yet little is known about the impact of sleep disturbances in children with type 1 diabetes. The current study sought to characterize sleep in children with type 1 diabetes and in their parents and to examine the associations between child sleep, glycemic control and adherence, parent sleep and well-being, parental fear of hypoglycemia, and nocturnal caregiving behavior.
Methods: Surveys were emailed to parents of 2- to 12-year-old participants in the Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Exchange clinic registry. Clinical data were obtained from the registry for the 515 respondents.
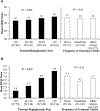
Results: In our sample, 67% of children met criteria for poor sleep quality. Child sleep quality was related to glycemic control (HbA1c of 7.9% [63 mmol/mol] in children with poor sleep quality vs 7.6% [60 mmol/mol] in children with non-poor sleep quality; P < 0.001) but not mean frequency of blood glucose monitoring (BGM) (7.6 times/day vs 7.4 in poor/non-poor quality; P = 0.56). Associations were similar for sleep duration. Children with poor sleep quality were more likely to experience severe hypoglycemia (4% in children with poor sleep quality vs 1% in children with non-poor sleep quality; P = 0.05) and more likely to experience DKA (7% vs 4%, respectively; P < 0.001). Poorer child sleep quality was associated with poorer parental sleep quality, parental well-being, and fear of hypoglycemia (P < 0.001 for all). Child sleep was not related to the use of diabetes-related technology (CGM, insulin pump).
Conclusions: Sleep may be a modifiable factor to improve glycemic control and reduce parental distress.
Keywords: Glycemic control; Sleep quality; Type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Owens J. Classification and epidemiology of childhood sleep disorders. Prim Care 2008;35(3):533–46. vii. - PubMed
-
- Mindell JA, Kuhn B, Lewin DS, et al. American Academy of Sleep M. Behavioral treatment of bedtime problems and night wakings in infants and young children. Sleep 2006;29(10):1263–76. - PubMed
-
- Monaghan MC, Hilliard ME, Cogen FR, et al. Nighttime caregiving behaviors among parents of young children with type 1 diabetes: associations with illness characteristics and parent functioning. Fam Syst Health 2009;27(1): 28–38. - PubMed
-
- Association AD. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2016. Diabetes Care 2016;39(Suppl 1):S1–106. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

