Use of an integrated strip-free blood glucose monitoring system increases frequency of self-monitoring and improves glycemic control: Results from the ExAct study
- PMID: 29159096
- PMCID: PMC5684965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2014.08.003
Use of an integrated strip-free blood glucose monitoring system increases frequency of self-monitoring and improves glycemic control: Results from the ExAct study
Abstract
Aims: We investigated the impact of using an integrated, strip-free system compared to the use of single-strip systems on testing frequency and glycemic control in individuals with insulin-treated diabetes.
Methods: This multinational, comparative, cluster-randomized, observational study included 311 patients with type 1 and insulin-treated type 2 diabetes who were performing SMBG at suboptimal frequencies. Sites were cluster-randomized to "integrated strip-free" system (EXP group) or any "single-strip" system (CNL group). Testing frequency and HbA1c were measured at baseline, 12 weeks and 24 weeks.
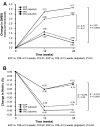
Results: At week 24, the EXP group showed an increase in SMBG frequency from baseline of 4.17 tests/week (95% CI 2.76, 5.58) compared with an increase of 0.53 tests/week (95% CI -0.73, 1.79) among CNL patients, resulting in a between-group difference of 3.63 tests/week (p < 0.0002). Mixed-effects models for repeated measurements (MMRM) controlling for baseline frequency of testing, country and clinical site confirmed a higher SMBG testing frequency in the EXP group compared to the CNL group, with a between-group difference of 2.70 tests/week (p < 0.01). Univariate analysis showed greater HbA1c reductions in the EXP group than CNL group: -0.44% (95% CI -0.59, -0.29) vs. -0.13% (95% CI -0.27, 0.01), respectively, p < 0.0002. MMRM analyses confirmed these HbA1c reductions. A greater percentage of EXP than CNL patients achieved HbA1c reductions of ≥0.5%: 45.1% vs. 29.1%, respectively, p < 0.01.
Conclusions: The use of an integrated, strip-free SMBG system improved testing adherence and was associated with improvements in glycemic control.
Keywords: Adherence; Glycemic control; HbA1c; Insulin; Integrated strip-free system; SMBG; Self-monitoring of blood glucose; Testing frequency; Type 1 diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Global guideline on self-monitoring of blood glucose in non-insulin treated type 2 diabetes. International Diabetes Federation; 2009. http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/SMBG_EN2.pdf Available from: Accessed 03.11.13.
-
- Parkin C.G., Buskirk A., Hinnen D.A., Axel-Schweitzer M. Results that matter: structured vs. unstructured self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;97:6–15. - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed
-
- Schutt M., Kern W., Krause U., Busch P., Dapp A., Grziwotz R. Is the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose related to long-term metabolic control? Multicenter analysis including 24,500 patients from 191 centers in Germany and Austria. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2006;114:384–388. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources