Teaching an old pET new tricks: tuning of inclusion body formation and properties by a mixed feed system in E. coli
- PMID: 29159587
- PMCID: PMC5756567
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-017-8641-6
Teaching an old pET new tricks: tuning of inclusion body formation and properties by a mixed feed system in E. coli
Abstract
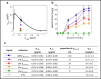
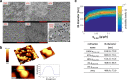
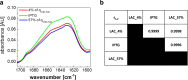
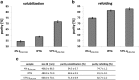
Against the outdated belief that inclusion bodies (IBs) in Escherichia coli are only inactive aggregates of misfolded protein, and thus should be avoided during recombinant protein production, numerous biopharmaceutically important proteins are currently produced as IBs. To obtain correctly folded, soluble product, IBs have to be processed, namely, harvested, solubilized, and refolded. Several years ago, it was discovered that, depending on cultivation conditions and protein properties, IBs contain partially correctly folded protein structures, which makes IB processing more efficient. Here, we present a method of tailored induction of recombinant protein production in E. coli by a mixed feed system using glucose and lactose and its impact on IB formation. Our method allows tuning of IB amount, IB size, size distribution, and purity, which does not only facilitate IB processing, but is also crucial for potential direct applications of IBs as nanomaterials and biomaterials in regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Escherichia coli BL21(DE3); Inclusion body properties; Inclusion body purity; Inclusion body size; Lactose; pET expression system.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY. Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci. 2006;61(3):876–885. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2005.03.031. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

