Exposure-response relationship of certolizumab pegol induction and maintenance therapy in patients with Crohn's disease
- PMID: 29159893
- PMCID: PMC5765392
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.14421
Exposure-response relationship of certolizumab pegol induction and maintenance therapy in patients with Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: Therapeutic drug monitoring may optimize therapy for Crohn's disease (CD).
Aim: To use a population pharmacokinetic model that accounts for the time-varying nature of covariates to simulate certolizumab pegol (CZP) concentrations to evaluate the exposure-response relationship for CZP in Crohn's disease.
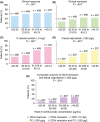
Methods: Adults (N = 2157) with Crohn's disease were treated with CZP in nine clinical trials. Simulated CZP concentrations were compared to outcomes at weeks 6 and 26, including Crohn's disease activity index (CDAI) response (decrease from baseline ≥ 100 points), remission (CDAI ≤ 150), C-reactive protein (CRP) ≤ 5 mg/L, faecal calprotectin (FC) ≤ 250 μg/g, and a composite endpoint of CDAI ≤ 150 and FC ≤ 250 μg/g. Multivariable analyses identified covariates associated with outcomes and receiver operating characteristic analyses determined optimal CZP concentrations.
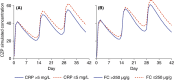
Results: CZP concentrations at weeks 2, 4 and 6 were higher in patients with clinical response, remission, CRP ≤ 5 mg/L or FC ≤ 250 μg/g at week 6 than without. In multivariable analyses, higher CZP concentrations at week 6 were associated with the composite outcome at weeks 6 and 26 (P < .001). Although the exposure-response relationship varied among patients, approximate CZP concentrations of at least 36.1 μg/mL (positive predictive value [PPV] 22.8% and negative predictive value [NPV] 92.7%) and at least 14.8 μg/mL (PPV 28.0% and NPV 90.4%) at weeks 6 and 12 were associated with weeks 6 and 26 outcomes.
Conclusions: An exposure-response relationship was apparent for CZP in Crohn's disease and achieving higher CZP concentrations may increase the likelihood of attaining efficacy outcomes, but this remains to be evaluated prospectively.
© 2017 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Allez M, et al. Association between plasma concentrations of certolizumab pegol and endoscopic outcomes of patients with Crohn's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;12:423‐431.e1. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Stoinov S, et al. Certolizumab pegol for the treatment of Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:228‐238. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Lee SD, Randall C, et al. Long‐term safety and efficacy of certolizumab pegol in the treatment of Crohn's disease: 7‐year results from the PRECiSE 3 study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:903‐916. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber S, Khaliq‐Kareemi M, Lawrance IC, et al. Maintenance therapy with certolizumab pegol for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:239‐250. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Thomsen OØ, Schreiber S, et al. Continuous therapy with certolizumab pegol maintains remission of patients with Crohn's disease for up to 18 months. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:600‐609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
