Proton pump inhibitors for functional dyspepsia
- PMID: 29161458
- PMCID: PMC6485982
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011194.pub3
Proton pump inhibitors for functional dyspepsia
Abstract
Background: Functional dyspepsia (FD or non-ulcer dyspepsia) is defined as continuous or frequently recurring epigastric pain or discomfort for which no organic cause can be found. Acid suppressive therapy, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), has been proposed as a therapeutic option in FD, but its efficacy remains controversial. While PPIs are generally considered safe and well tolerated, they have been associated with adverse events, especially in the long term. For this reason, decisions on whether to initiate or continue PPI therapy should be made based on an appropriate clinical indication. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review to evaluate whether PPI therapy provides symptomatic relief in FD.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy of proton pump inhibitors in the improvement of global symptoms of dyspepsia and quality of life compared to placebo, H2 receptor antagonists or prokinetics, in people with functional dyspepsia.
Search methods: We searched in the following electronic databases: the Cochrane Library (to May 2017), MEDLINE (OvidSP; to May 2017), Embase (OvidSP; to May 2017), and SIGLE grey literature (up to May 2017) and clinical trial registries; we handsearched abstracts from conferences up to May 2017. We screened non-systematic reviews, systematic reviews and guidelines to identify any additional trials. We contacted trialists to obtain missing information.
Selection criteria: All randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing any PPI with placebo, H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs) or prokinetics for the treatment of FD of at least two weeks' duration. Participants were adults (aged 16 years or greater) with an adequate diagnosis of FD (any validated criteria such as Rome I, II, III or Lancet Working Group).
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed eligibility and trial quality, and extracted data. We collected data on dyspeptic symptoms, quality of life and number of overall adverse events. Specific adverse events were beyond the scope of this review.
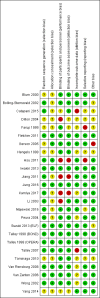
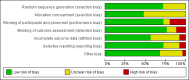
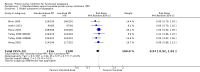
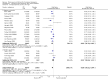
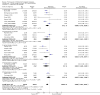
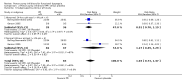
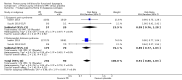
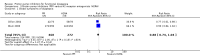
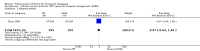
Main results: We identified 25 RCTs from 27 papers (with 8453 participants) studying the effect of PPIs versus placebo, H2RAs or prokinetics for improvement of global symptoms of dyspepsia and quality of life in people with FD. Low-dose PPIs had similar efficacy as standard-dose PPIs, therefore we combined these subgroups for the analysis. PPI was more effective than placebo at relieving overall dyspepsia symptoms in people with FD (risk ratio (RR) 0.88, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.82 to 0.94; participants = 6172; studies = 18; number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 11; moderate quality evidence). PPIs may have little or no effect compared with H2RAs (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.04; participants = 740; studies = 2; low quality evidence), and may be slightly more effective than prokinetics (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.81 to 0.99; participants = 1033; studies = 5; NNTB 16; low quality evidence) at relieving overall dyspepsia symptoms in people with FD. PPIs plus prokinetics have probably little or no effect compared with PPIs alone at relieving overall dyspepsia symptoms (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.08; participants = 407; studies = 2; moderate quality evidence).There was no difference when subgrouped by Helicobacter pylori status, country of origin, or presence of reflux or Rome III subtypes. There were no differences in the number of adverse events observed between PPIs and any of the other treatments. There were fewer adverse events in the combination of PPI plus prokinetics compared to prokinetics alone (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.93; participants = 407; studies = 2; moderate quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: There is evidence that PPIs are effective for the treatment of FD, independent of the dose and duration of treatment compared with placebo. PPIs may be slightly more effective than prokinetics for the treatment of FD; however, the evidence is scarce. The trials evaluating PPIs versus prokinetics are difficult to interpret as they are at risk of bias. Although the effect of these drugs seems to be small, the drugs are well tolerated.
Conflict of interest statement
MIPS: none known.
YY: none known.
AH: none known.
PB: none known.
PM has acted as a consultant and/or received speaker fees from Allergan, Shire and Lupin none of which directly or indirectly profit from PPI therapy. He also has received a research grant from Takeda to evaluate the diet and microbiome in IBS and IBD as part of the IMAGINE network but this company does sell a PPI.
Figures













Update of
-
Proton pump inhibitors for functional dyspepsia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 8;3(3):CD011194. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011194.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11:CD011194. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011194.pub3. PMID: 28271513 Free PMC article. Updated.
Comment in
-
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS FOR FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA.Gastroenterol Nurs. 2019 Nov/Dec;42(6):508-509. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0000000000000486. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31770354 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Blum 2000 {published data only}
Bolling‐Sternevald 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bolling‐Sternevald E, Lauritsen K, Aalykke C, Havelund T, Knudsen T, Unge P, et al. Effect of profound acid suppression in functional dyspepsia: a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2002;37(12):1395‐402. - PubMed
Catapani 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Catapani W, Guedes FS. A clinical trial assessing the efficacy of a therapeutic encounter versus traditional consultation in the management of functional dyspepsia. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2015;110(Suppl 1s):S751‐2.
Dillon 2004 {published data only}
-
- Dillon JF, Finch PJ, Baxter G. A comparison of lansoprazole vs ranitidine in the treatment of functional ulcer‐like dyspepsia as defined by the Rome II criteria. Gut 2004;53(Suppl VI):A285.
Farup 1999 {published data only}
-
- Farup PG, Hovde O, Torp R, Wetterhus S. Patients with functional dyspepsia responding to omeprazole have a characteristic gastro‐oesophageal reflux pattern. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1999;34(6):575‐9. - PubMed
Fletcher 2011 {published data only}
-
- Fletcher J, Derakhshan MH, Jones GR, Wirz AA, McColl KEL. BMI is superior to symptoms in predicting response to proton pump inhibitor: randomised trial in patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms and normal endoscopy. Gut 2011;60:442‐8. - PubMed
Gerson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gerson LB, Triadafilopoulos G. A prospective study of oesophageal 24‐h ambulatory pH monitoring in patients with functional dyspepsia. Digestive and Liver Disease 2005;37(2):87‐91. - PubMed
Hengels 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hengels KJ. Therapeutic efficacy of 15mg lansoprazole mane in 269 patients suffering from non‐ulcer dyspepsia (NUD): a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind study. Gut 1998;43 (Suppl 2):A89.
Hsu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hsu YC, Liou JM, Yang TH, Hsu WL, Lin HJ, Wu HT, et al. Proton pump inhibitor versus prokinetic therapy in patients with functional dyspepsia: is therapeutic response predicted by Rome III subgroups?. Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;46:183‐90. - PubMed
Iwakiri 2013 {published data only}
-
- Iwakiri R, Tominaga K, Furuta K, Inamori M, Furuta T, Masuyama H, et al. Randomised clinical trial: rabeprazole improves symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia in Japan. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2013;16(9):547‐50. - PubMed
Jiang 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jiang Q, Ding X, Zhang S, Wang H, Yu X, Xie S. Comparison of mosapride and pantoprazole in treating functional dyspepsia. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 2011;16(9):254‐63.
Jung 2016 {published data only}
Kamiya 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kamiya T, Shikano M, Hirata Y, Mizushima T, Murakami K, Shimura, et al. A multicenter open‐label randomized trial comparing rabeprazole versus itopride in Japanese functional dyspepsia: the NAGOYA Study. Gastroenterology 2011;140(5):S189.
-
- Kamiya T, Shikano M, Mizushima T, Hirata Y, Murakami K, Shimura T, et al. T1095 comparison of rabeprazole and itopride in the treatment of functional dyspepsia sub‐analysis: Nagoya multicentre randomised comparative trial. Gastroenterology 2010;138(5):S486‐7.
-
- Kamiya T, Shikano M, Ozeki K, Hirata Y, Mizoshita T, Mori Y, et al. Are there any differences among predictive response factors for a proton pump inhibitor and prokinetics? Sub‐analysis of a multicenter open‐label randomized trial comparing rabeprazole versus itopride in Japanese functional dyspepsia: the NAGOYA study. Gastroenterology 2012;142(5 Suppl 1):S‐468.
Li 2003 {published data only}
-
- Li Z, Guomin X, Yiqi D, Wenzhong L, Xiao SD. Low‐dose omeprazole treatment of functional dyspepsia. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology 2003;6:337‐9.
Majewski 2016 {published data only}
-
- Majewski M, Sarosiek I, Cooper CJ, Wallner G, McCallum RW, Edlavitch SA, et al. Gastric pH and therapeutic responses to exsomeprazole in patients with functional dyspepsia: potential clinical implications. American Journal of the Medical Sciences 2016;352(6):582‐92. - PubMed
Peura 2004 {published data only}
-
- Peura DA, Kovacs TO, Metz DC, Siepman N, Pilmer BL, Talley NJ. Lansoprazole in the treatment of functional dyspepsia: two double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trials. American Journal of Medicine 2004;116(11):740‐8. - PubMed
Suzuki 2013 (ELF) {published data only}
-
- Suzuki H, Kusunoki H, Kamiya T, Futagami S, Yamaguchi Y, Nishizawa T, et al. Effect of lansoprazole on the epigastric symptoms of functional dyspepsia (ELF study): a multicentre, prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. United European Gastroenterology Journal 2013;1(6):445‐52. - PMC - PubMed
Talley 1998 (BOND) {published data only}
-
- Talley NJ, Meineche‐Schmidt V, Pare P, Duckworth M, Raisanen P, Pap A, et al. Efficacy of omeprazole in functional dyspepsia: double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trials (the BOND and OPERA studies). Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1998;12:1055‐65. - PubMed
Talley 1998 (OPERA) {published data only}
-
- Talley NJ, Meineche‐Schmidt V, Pare P, Duckworth M, Raisanen P, Pap A, et al. Efficacy of omeprazole in functional dyspepsia: double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trials (the BOND and OPERA studies). Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1998;12:1055‐65. - PubMed
Talley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Talley NJ, Vakil N, Lauritsen K, Zanten VS, Flook N, Bolling‐Sternevald E, et al. Randomized‐controlled trial of esomeprazole in functional dyspepsia patients with epigastric pain or burning: does a 1‐week trial of acid suppression predict symptom response?. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007;26(5):673‐82. - PubMed
Tominaga 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tominaga K, Suzuki H, Umegaki E, Kusunoki H, Tomotsugu N, Higuchi K, et al. Rabeprazole improves the symptoms of functional dyspepsia ‐ a double blind randomized placebo‐controlled multi‐center trial in Japan: the CAESAR Study. Gastroenterology 2010;138(5 Suppl 1):S55.
Van Rensburg 2008 {published data only}
-
- Rensburg C, Berghofer P, Enns R, Dattani ID, Maritz JF, Gonzalez Carro P, et al. Efficacy and safety of pantoprazole 20 mg once daily treatment in patients with ulcer‐like functional dyspepsia. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2008;24(7):2009‐18. - PubMed
Van Zanten 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zanten SV, Armstrong D, Chiba N, Flook N, White RJ, Chakraborty B, et al. Esomeprazole 40 mg once a day in patients with functional dyspepsia: the randomized, placebo‐controlled "ENTER" trial. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2006;101:2096‐106. - PubMed
Wong 2002 {published data only}
Yang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yang ZY. Efficacy and safety of pantoprazole sodium enteric coated tablets combined with mosapride in treatment of functional dyspepsia. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2014;22(29):4514‐18.
References to studies excluded from this review
Almazar 2015 {published data only}
-
- Almazar AE, Saito YA, Locke G, Camillieru M, Burton DD, Bouras EP, et al. Is proton pump inhibitor use associated with delayed gastric emptying in functional dyspepsia subjects?. Gastroenterology 2015;148(4):S888.
Bolling‐Sternvald 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bolling‐Sternevald E, Lauritsen K, Talley NJ, Junghard O, Glise H. Is it possible to predict treatment response to a proton pump inhibitor in functional dyspepsia?. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2003;18(1):117‐24. - PubMed
Burkov 2009 {published data only}
-
- Burkov SG, Arutiunov AT, Okoemov MN, Anokhina LN, Egorova NV, Makukh EA, et al. Effectiveness of Ultop 10 mg using at treatment of functional (nonulcer) dyspepsia syndrome. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Gastroenterologiia [Experimental & Clinical Gastroenterology] 2009;6:122‐6. - PubMed
Bytzer 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bytzer P, Hansen JM, Rune S, Bonnevie O, Breinstrup H, Funch‐Jensen P, et al. Identifying responders to acid suppression in dyspepsia using a random starting day trial. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2000;14(11):1485‐94. - PubMed
Cheung 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cheung CK, Lee Y, Chan Y, Chan A, Law WT, Lan LL, et al. The effect of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) on plasma 5‐hydroxytryptamine (5‐HT) levels in patients with functional dyspepsia (FD): a double‐blind randomized control trial. Gastroenterology 2013;144(5):S679.
Chuang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chuang CH, Sheu BS, Yang HB, Wu JJ, Lin XZ. Ranitidine bismuth citrate or omeprazole‐based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in Helicobacter pylori‐infected non‐ulcer dyspepsia. Digestive and Liver Disease 2001;33(2):125‐30. - PubMed
Delaney 2008 {published data only}
Fan 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fan YH, Cai LJ, Xu GP. Treatment of functional dyspepsia by Chinese medical syndrome typing: a randomized control research. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine] 2012;32(12):1592‐7. - PubMed
Fransen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fransen GA, Mesters I, Muris JW, Marrewijk CJ, Mujakovic S, Laheij RJ, et al. Patient adherence to prescribed medication instructions for dyspepsia: the DIAMOND study. European Journal of General Practice 2012;18(2):79‐85. - PubMed
Goves 1998 {published data only}
-
- Goves J, Oldring JK, Kerr D, Dallara RG, Roffe EJ, Powell JA, et al. First line treatment with omeprazole provides an effective and superior alternative strategy in the management of dyspepsia compared to antacid/alginate liquid: a multicentre study in general practice. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1998;12(2):147‐57. - PubMed
Guo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Guo LK, Zhang CX, Guo XF. Long‐term efficacy and safety research on functional dyspepsia treated with electroacupuncture and Zhizhu Kuanzhong capsule. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu [Chinese Acupuncture & Moxibustion] 2011;31(12):1071‐7. - PubMed
Ivanova 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ivanova NG. Inhibitors of proton pump in the treatment of non‐ulcer functional dyspepsia of the reflux‐like type. Eksperimental'naia i Klinicheskaia Gastroenterologiia [Experimental & Clinical Gastroenterology] 2002;101(2):35‐6. - PubMed
Jones 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jones RH, Baxter G. Lansoprazole 30 mg daily versus ranitidine 150 mg b.d. in the treatment of acid‐related dyspepsia in general practice. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1997;11(3):541‐6. - PubMed
Jones 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jones R, Crouch SL. Low‐dose lansoprazole provides greater relief of heartburn and epigastric pain than low‐dose omeprazole in patients with acid‐related dyspepsia. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1999;13(3):413‐9. - PubMed
Kamada 2013 {published data only}
Leung 2007 {published data only}
-
- Leung WK, Wu JC, Chan FK, Fung SS, Wong VW, Hui AJ, et al. Initial treatment with lansoprazole in young dyspeptic patients with negative urea breath test result: a randomized controlled trial with 12‐month follow‐up. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2007;102(7):1483‐8. - PubMed
Lewin van den Broek 2001 {published data only}
Madsen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Madsen LG, Bytzer P. Reproducibility of a symptom response to omeprazole therapy in functional dyspepsia evaluated by a random‐starting‐day trial design. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;20(3):365‐72. - PubMed
Madsen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Madsen LG, Bytzer P. Symptomatic response to blocked and unblocked pentagastrin stimulation in functional dyspepsia. Comparison of responders and non‐responders to omeprazole identified in a single‐subject trial model. Digestive Diseases (Basel, Switzerland) 2008;26(3):237‐42. - PubMed
Mazure 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mazure PA. Gastric acid secretion inhibitors: H2 receptor antagonists (H2RA), proton pump inhibitors (PPI) or acid pump antagonists (APA). Acta Gastroenterologica Latinoamericana 1996;26(4):263‐5. - PubMed
Meineche‐Schmidt 1999 {published data only}
-
- Meineche‐Schmidt V, Talley NJ, Pap A, Kordecki H, Schmid V, Ohlsson L, et al. Impact of functional dyspepsia on quality of life and health care consumption after cessation of antisecretory treatment. A multicentre 3‐month follow‐up study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1999;34(6):566‐74. - PubMed
Meineche‐Schmidt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Meineche‐Schmidt V, Christensen E. Which dyspepsia patients will benefit from omeprazole treatment? Analysis of a Danish multicenter trial. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2000;95(10):2777‐83. - PubMed
Meineche‐Schmidt 2004 {published data only}
-
- Meineche‐Schmidt V. Classification of dyspepsia and response to treatment with proton‐pump inhibitors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;20(10):1171‐9. - PubMed
Miwa 2015 {published data only}
-
- Miwa H, Haruma K, Sakamoto S, Sanada K, Hiroi S, Kinoshita Y. Demography and treatment response in patients with predominant non‐erosive reflux disease or functional dyspepsia. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2015;30(5):834‐41. - PubMed
Mönnikes 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mönnikes H, Schmidtmann M. Irritable bowel disease with flatulence: is the breath test for carbohydrate malabsorption obligatory?. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (1946) 2009;134(37):1828. - PubMed
Mönnikes 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mönnikes H, Schwan T, Rensburg C, Straszak A, Theek C, Sander P, et al. Randomised clinical trial: sustained response to PPI treatment of symptoms resembling functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome in patients suffering from an overlap with erosive gastro‐oesophageal reflux disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2012;35(11):1279‐89. - PubMed
Nagahara 2015 {published data only}
-
- Nagahara A, Miwa H, Asaoka D, Shimada Y, Sasaki H, Matsumoto K, et al. Pretreatment prediction of symptom response to proton pump inhibitor therapy. Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2015;Suppl 1:25‐30. - PubMed
Pilichiewicz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Pilichiewicz AN, Andrews JM, Goess C, McMahon J, Fraser RJ, Beilby J, et al. A preliminary analysis of the effect Iberogast, Nexium, dual Iberogast + Nexium or dual placebo on symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26(s4):85. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06826.x] - DOI
Rabeneck 2001 (SODA) {published data only}
-
- Rabeneck L, Cook KF, Wristers K, Souchek J, Menke T, Wray NP. SODA (severity of dyspepsia assessment): a new effective outcome measure for dyspepsia‐related health. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2001;54(8):755‐65. - PubMed
Reimer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Reimer C, Bytzer P. Discontinuation of long‐term proton pump inhibitor therapy in primary care patients: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial in patients with symptom relapse. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2010;22(10):1182‐8. - PubMed
Rui 2015 {published data only}
-
- Rui J, Kang J, Xiu‐Li Z, Yanqing L. Randomized clinical study on functional dyspepsia treatment with herbal preparation puyuanhewei and therapeutic response evaluation by endomicroscopy. Gastroenterology 2015;148(4 Suppl 1):S891.
Sakaguchi 2012 {published data only}
Sakurai 2012 (J‐FOCUS) {published data only}
Schwartz 2001 {published data only}
-
- Schwartz MP, Samsom M, Berge Henegouwen GP, Smout AJ. Effect of inhibition of gastric acid secretion on antropyloroduodenal motor activity and duodenal acid hypersensitivity in functional dyspepsia. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2001;15(12):1921‐8. - PubMed
Theodoropoulos 2009 {published data only}
-
- Theodoropoulos I, Karakoidas C, Papamichael K, Smyrnidis A, Archavlis EJ, Mantzaris GJ. A lyophilized form of S. boulardii enhances the effect of omeprazole‐triple therapy in patients with organic or functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2009;Suppl 1:A343.
van Zanten 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zanten SV, Armstrong D, Barkun A, Junghard O, White RJ, Wiklund IK. Symptom overlap in patients with upper gastrointestinal complaints in the Canadian Confirmatory Acid Suppression Test (CAST) study: further psychometric validation of the reflux disease questionnaire. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2007;25(9):1087‐97. - PubMed
Veldhuyzen van Zanten 2005 {published data only}
-
- Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Chiba N, Armstrong D, Barkun A, Thomson A, Smyth S, et al. A randomized trial comparing omeprazole, ranitidine, cisapride, or placebo in Helicobacter pylori negative, primary care patients with dyspepsia: the CADET‐HN Study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2005;100(7):1477‐88. - PubMed
Zeng 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zeng J, Zuo XL, Li YQ, Wei W, Lv GP. Tegaserod for dyspepsia and reflux symptoms in patients with chronic constipation: an exploratory open‐label study. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2007;63(6):529‐36. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Puttapitakpong 2016 {published data only}
-
- Puttapitakpong C, Jearjesdakul J. Effectiveness of curcuma longa linn compared with omeprazole on treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2016;150(4 (Suppl 1)):S 43.
Yamawaki 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yamawaki H, Futagami S, Kawagoe T, Maruki Y, Hashimoto S, Nagoya H, et al. Improvement of meal‐related symptoms and epigastric pain in patients with functional dyspepsia treated with acotiamide was associated with acylated ghrelin levels in Japan. Neurogastroenterology and Motility 2016;28(7):1037‐47. - PubMed
Additional references
Abraham 2004
-
- Abraham NS, Moayyedi P, Daniels B, Veldhuyzen Van Zanten SJ. Systematic review: the methodological quality of trials affects estimates of treatment efficacy in functional (non‐ulcer) dyspepsia. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2004;19(6):631‐41. - PubMed
Abramowitz 2016
-
- Abramowitz J, Thakkar P, Isa A, Truong A, Park C, Rosenfeld RM. Adverse event reporting for proton pump inhibitor therapy: an overview of systematic reviews. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery 2016;155(4):547‐54. - PubMed
Barbera 1995
-
- Barbera R, Feinle C, Read NW. Nutrient specific modulation of gastric mechanosensitivity in patients with functional dyspepsia. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 1995;40(8):1636‐41. - PubMed
Bekhti 1979
-
- Bekhti A, Rutgeerts L. Domperidone in the treatment of functional dyspepsia in patients with delayed gastric emptying. Postgraduate Medical Journal 1979;55(Suppl 1):30‐2. - PubMed
Bercik 2000
-
- Bercík P, Verdú EF, Armstrong D, Idström JP, Cederberg C, Markert M, et al. The effect of ammonia on omeprazole‐induced reduction of gastric acidity in subjects with Helicobacter pylori infection. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2000;95(4):947‐55. - PubMed
Blum 1998
-
- Blum AL, Talley NJ, O'Moráin C, van Zanten SV, Labenz J, Stolte M, et al. Lack of effect of treating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. Omeprazole plus clarithromycin and amoxicillin effect one year after treatment (OCAY) study group. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;339(26):1875‐81. - PubMed
Bolling‐Sternevald 2003
-
- Bolling‐Sternevald E, Lauritsen K, Talley NJ, Junghard O, Glise H. Is it possible to predict treatment response to a proton pump inhibitor in functional dyspepsia?. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2003;18(1):117‐24. - PubMed
Calvert 2002
-
- Calvert EL, Houghton LA, Cooper P, Morris J, Whorwell PJ. Long‐term improvement in functional dyspepsia using hypnotherapy. Gastroenterology 2002;123(6):1778‐85. - PubMed
Camillieri 2013
-
- Camillieri M, Stanghellini V. Current management strategies and emerging treatments for functional dyspepsia. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2013;10(3):187‐94. - PubMed
Chen 2000
-
- Chen JD, Ke MY, Lin XM, Wang Z, Zhang M. Cisapride provides symptomatic relief in functional dyspepsia associated with gastric myoelectrical abnormality. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2000;14(8):1041‐7. - PubMed
Colin‐Jones 1988
-
- Colin‐Jones DG, Bloom B, Bodemar G, Crean G, Freston J, Gugler R, et al. Management of dyspepsia: report of a working party. Lancet 1988;331(8585):576‐9. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Alman DG, Cochrane Statistics Methods Group. Chapter 9.4.5.2: Meta‐analysis of change scores. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Drossman 1999
-
- Drossman DA, Corazziari E, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE. Rome II: a multinational consensus document on functional gastrointestinal disorders ‐ functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain. Gut 1999;45(2):ii‐43.
Drossman 2006
-
- Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1377‐90. - PubMed
Froehlich 2001
-
- Froehlich F, Gonvers JJ, Wietlisbach V, Burnand B, Hildebrand P, Schneider C, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment does not benefit patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2001;96(8):2329‐36. - PubMed
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H, 2008.
GraphPad [Computer program]
-
- GraphPad Software. GraphPad Software. Version 5.04. La Jolla (CA): GraphPad Software, 2010.
Hamilton 2000
-
- Hamilton J, Guthrie E, Creed F, Thompson D, Tomenson B, Bennett R, et al. A randomized controlled trial of psychotherapy in patients with chronic functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2000;119(3):661‐9. - PubMed
Hansen 1998
-
- Hansen JM, Bytzer P, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB. Placebo‐controlled trial of cisapride and nizatidine in unselected patients with functional dyspepsia. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1998;93(3):368‐74. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Holtmann 2002
-
- Holtmann G, Gschossmann J, Mayr P, Talley NJ. A randomized placebo‐controlled trial of simethicone and cisapride for the treatment of patients with functional dyspepsia. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2002;16(9):1641‐8. - PubMed
Johnson 2013
-
- Johnson DA, Oldfield EC. Reported side effects and complications of long‐term proton pump inhibitor use. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;11(5):458‐64. - PubMed
Kwok 2013
-
- Kwok CS, Jeevanantham V, Dawn B, Loke YK. No consistent evidence of differential cardiovascular risk amongst proton‐pump inhibitors when used with clopidogrel: meta‐analysis. International Journal of Cardiology 2013;167(3):965‐74. [PUBMED: 22464478] - PubMed
Lacy 2012
Lacy 2013
-
- Lacy BE, Weiser KT, Kennedy MD, Crowell MD, Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia: the economic impact to patients. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2013;38(2):170‐7. - PubMed
McColl 1998
-
- McColl K, Murray L, El‐Omar E, Dickson A, El‐Nujumi A, Wirz A, et al. Symptomatic benefit from eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;339(26):1869‐74. - PubMed
Moayyedi 2003
Moayyedi 2006
Moayyedi 2011
Overland 2014
-
- Overland MK. Dyspepsia. Medical Clinics of North America 2014;98:549‐64. - PubMed
Reference Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Thomson ISI ResearchSoft. Reference Manager. Version 12.0.3. Copenhagen: Thomson ISI ResearchSoft, 2014.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robinson 2004
-
- Robinson M. Review article: the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of proton pump inhibitors ‐ overview and clinical implications. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;20(Suppl 6):1‐10. - PubMed
Savarino 2017
-
- Savarino V, Dulbecco P, Bortoli N, Ottonello A, Savarino E. The appropriate use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): need for a reappraisal. European Journal of Internal Medicine 2017;37:19‐24. - PubMed
Scarpignato 2016
-
- Scarpignato C, Gatta L, Zullo A, Blandizzi C, SIF‐AIGO‐FIMMG Group, Italian Society of Pharmacology, the Italian Association of Hospital Gastroenterologists, the Italian Federation of General Practitioners. Effective and safe proton pump inhibitor therapy in acid‐related diseases ‐ a position paper addressing benefits and potential harms of acid suppression. BMC Medicine 2016;14(1):179. - PMC - PubMed
Stanghellini 2016
-
- Stanghellini V, Chan FK, Hasler WL, Malagelada JR, Suzuki H, Tack J, et al. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology 2016;150:1380‐92. - PubMed
Suzuki 2011
Talley 1991
-
- Talley NJ. Drug treatment of functional dyspepsia. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1991;182:47‐60. - PubMed
Talley 1995
-
- Talley NJ. Functional dyspepsia ‐ should treatment be targeted on disturbed physiology?. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1995;9(2):107‐15. - PubMed
Talley 1999a
-
- Talley NJ, Janssens J, Lauritsen K, Rácz I, Bolling‐Sternevald E. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 months' follow up. The Optimal Regimen Cures Helicobacter Induced Dyspepsia (ORCHID) Study Group. BMJ 1999;318(7187):833‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Talley 1999b
-
- Talley NJ, Vakil N, Ballard ED 2nd, Fennerty MB. Absence of benefit of eradicating Helicobacter pylori in patients with non‐ulcer dyspepsia. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;341(15):1106‐11. - PubMed
Talley 2016
-
- Talley NJ, Walker M, Holtmann G. Functional dyspepsia. Current Opinions in Gastroenterology 2016;32(6):467‐73. - PubMed
Tett 2013
Van Outryve 1993
-
- Outryve M, Nutte N, Eeghem P. Efficacy of cisapride in functional dyspepsia resistant to domperidone or metoclopramide: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 1993;195:47‐52. - PubMed
Verdú 1995
Wang 2007
-
- Wang WH, Huang JQ, Zheng GF. Effects of proton pump inhibitors on functional dyspepsia: a meta‐analysis of randomized placebo‐controlled trials. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2007;5(2):178‐85. - PubMed
Wilhelm 2013
-
- Wilhelm S, Rjater R, Kale‐Pradhan PB. Perils and pitfalls of long‐term effects of proton pump inhibitors. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 2013;6(4):443‐51. - PubMed
Yang 2010
-
- Yang YX, Metz DC. Safety of proton pump inhibitor exposure. Gastroenterology 2010;139(4):115‐27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

