Integrating molecular and structural findings: Wnt as a possible actor in shaping cognitive impairment in Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- PMID: 29162129
- PMCID: PMC5696803
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-017-0723-0
Integrating molecular and structural findings: Wnt as a possible actor in shaping cognitive impairment in Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Abstract
Cornelia de Lange Syndrome (CdLS) is a choesinopathy: a severe genetic disorder caused by mutations in the cohesin complex genes. The phenotype is characterized by typical facial dysmorphism, growth impairment and multiorgan abnormalities including brain alterations. Wnt pathway is known to play a fundamental role in central nervous system development and it has been shown that Wnt pathway is disrupted in CdLS animal models and patients cells. In this review we investigate the possible link between Wnt pathway disruption and brain abnormalities in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome as such molecular impairment could lead to an abnormal embryonic development resulting in brain abnormalities (i.e. microcephaly, cerebellar hypoplasia, abnormal cortical development) in patients with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome.
Keywords: Brain abnormalities; Cornelia de Lange syndrome; Wnt pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
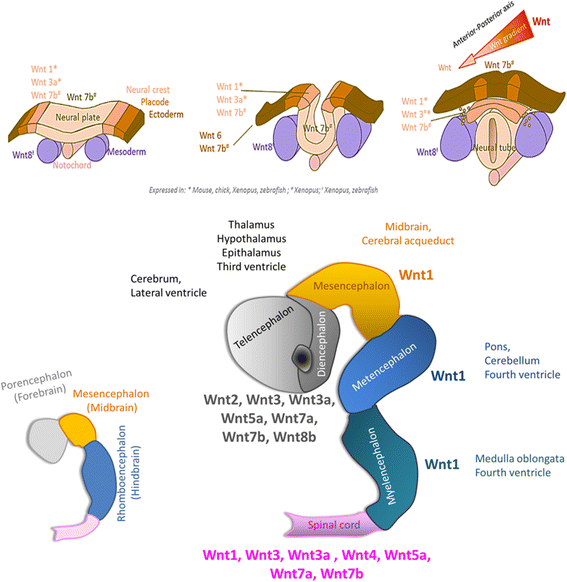
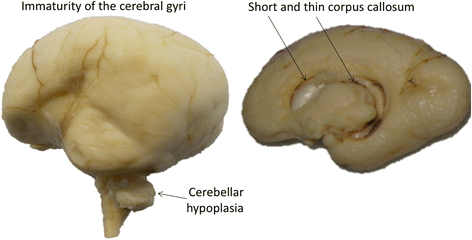
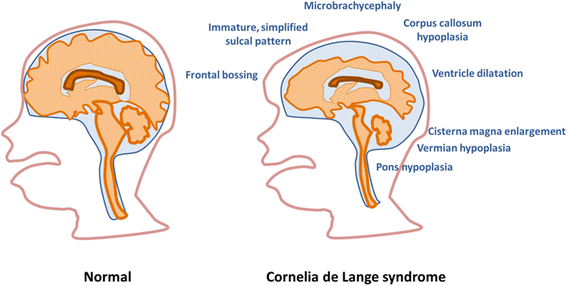
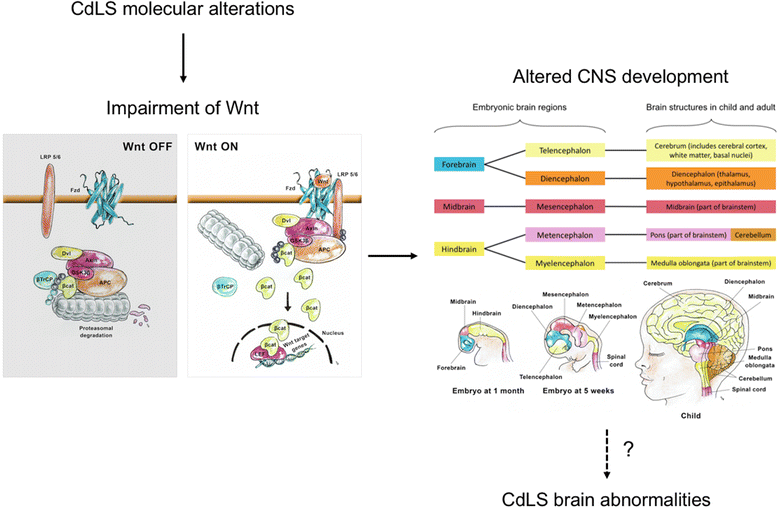
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

