Dynamic stress-related epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter during early development: The role of child maltreatment
- PMID: 29162170
- PMCID: PMC5726533
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579417001298
Dynamic stress-related epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter during early development: The role of child maltreatment
Abstract
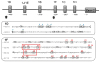
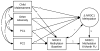
Epigenetics processes may play a vital role in the biological embedding of early environmental adversity and the development of psychopathology. Accumulating evidence suggests that maltreatment is linked to methylation of the glucocorticoid receptor gene, nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 1 (NR3C1), which is a key regulator of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. However, prior work has been exclusively cross-sectional, greatly constraining our understanding of stress-related epigenetic processes over time. In the current study, we examined the effect of maltreatment and other adversity on change in NR3C1 methylation among at-risk preschoolers to begin to characterize within-child epigenetic changes during this sensitive developmental period. Participants were 260 preschoolers (3-5 years old, 53.8% female), including 51.5% with moderate to severe maltreatment in the past 6 months. Child protection records, semistructured interviews, and parent reports were used to assess child stress exposure. Methylation of exons 1D and 1F of NR3C1 via saliva DNA were measured at two time points approximately 6 months apart. Results indicate that maltreated children evidence higher baseline levels of NR3C1 methylation, significant decreases in methylation over time, and then at follow-up, lower levels of methylation, relative to nonmaltreated preschoolers. Findings from the current study highlight the complex nature of stress-related epigenetic processes during early development.
Figures

References
-
- Barnett D, Manly JT, Cicchetti D. Defining child maltreatment: the interface between policy and research. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL, editors. Child abuse, child development, and social policy. Norwood, NJ: Ablex; 1993. pp. 7–73.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

