Whole Y-chromosome sequences reveal an extremely recent origin of the most common North African paternal lineage E-M183 (M81)
- PMID: 29162904
- PMCID: PMC5698413
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16271-y
Whole Y-chromosome sequences reveal an extremely recent origin of the most common North African paternal lineage E-M183 (M81)
Abstract
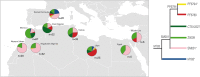
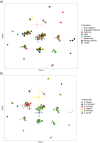
E-M183 (E-M81) is the most frequent paternal lineage in North Africa and thus it must be considered to explore past historical and demographical processes. Here, by using whole Y chromosome sequences from 32 North African individuals, we have identified five new branches within E-M183. The validation of these variants in more than 200 North African samples, from which we also have information of 13 Y-STRs, has revealed a strong resemblance among E-M183 Y-STR haplotypes that pointed to a rapid expansion of this haplogroup. Moreover, for the first time, by using both SNP and STR data, we have provided updated estimates of the times-to-the-most-recent-common-ancestor (TMRCA) for E-M183, which evidenced an extremely recent origin of this haplogroup (2,000-3,000 ya). Our results also showed a lack of population structure within the E-M183 branch, which could be explained by the recent and rapid expansion of this haplogroup. In spite of a reduction in STR heterozygosity towards the West, which would point to an origin in the Near East, ancient DNA evidence together with our TMRCA estimates point to a local origin of E-M183 in NW Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paternal lineages in Libya inferred from Y-chromosome haplogroups.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2015 Jun;157(2):242-51. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22705. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2015. PMID: 25677690
-
Sousse: extreme genetic heterogeneity in North Africa.J Hum Genet. 2015 Jan;60(1):41-9. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2014.99. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25471516
-
Rapidly mutating Y-STRs in rapidly expanding populations: Discrimination power of the Yfiler Plus multiplex in northern Africa.Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019 Jan;38:185-194. doi: 10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2019. PMID: 30419518
-
Toward a consensus on SNP and STR mutation rates on the human Y-chromosome.Hum Genet. 2017 May;136(5):575-590. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1805-8. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28455625 Review.
-
On the Forensic Use of Y-Chromosome Polymorphisms.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 17;13(5):898. doi: 10.3390/genes13050898. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic structure in the paternal lineages of South East Spain revealed by the analysis of 17 Y-STRs.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 26;9(1):5234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41580-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30914710 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting human North African gene-flow into its western coastal surroundings.Proc Biol Sci. 2019 May 15;286(1902):20190471. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.0471. Proc Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31039721 Free PMC article.
-
Y Haplogroup Diversity of the Dominican Republic: Reconstructing the Effect of the European Colonization and the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trades.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Sep 1;12(9):1579-1590. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa176. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32835369 Free PMC article.
-
Tierra Del Fuego: What Is Left from the Precolonial Male Lineages?Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;13(10):1712. doi: 10.3390/genes13101712. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292597 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-biased patterns shaped the genetic history of Roma.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 2;10(1):14464. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71066-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32879340 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

