Difference in Perseverative Errors during a Visual Attention Task with Auditory Distractors in Alpha-9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit Wild Type and Knock-Out Mice
- PMID: 29163062
- PMCID: PMC5676050
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00357
Difference in Perseverative Errors during a Visual Attention Task with Auditory Distractors in Alpha-9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit Wild Type and Knock-Out Mice
Abstract
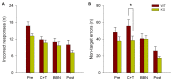
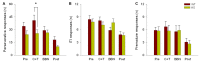
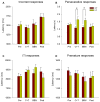
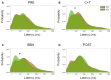
The auditory efferent system is a neural network that originates in the auditory cortex and projects to the cochlear receptor through olivocochlear (OC) neurons. Medial OC neurons make cholinergic synapses with outer hair cells (OHCs) through nicotinic receptors constituted by α9 and α10 subunits. One of the physiological functions of the α9 nicotinic receptor subunit (α9-nAChR) is the suppression of auditory distractors during selective attention to visual stimuli. In a recent study we demonstrated that the behavioral performance of alpha-9 nicotinic receptor knock-out (KO) mice is altered during selective attention to visual stimuli with auditory distractors since they made less correct responses and more omissions than wild type (WT) mice. As the inhibition of the behavioral responses to irrelevant stimuli is an important mechanism of the selective attention processes, behavioral errors are relevant measures that can reflect altered inhibitory control. Errors produced during a cued attention task can be classified as premature, target and perseverative errors. Perseverative responses can be considered as an inability to inhibit the repetition of an action already planned, while premature responses can be considered as an index of the ability to wait or retain an action. Here, we studied premature, target and perseverative errors during a visual attention task with auditory distractors in WT and KO mice. We found that α9-KO mice make fewer perseverative errors with longer latencies than WT mice in the presence of auditory distractors. In addition, although we found no significant difference in the number of target error between genotypes, KO mice made more short-latency target errors than WT mice during the presentation of auditory distractors. The fewer perseverative error made by α9-KO mice could be explained by a reduced motivation for reward and an increased impulsivity during decision making with auditory distraction in KO mice.
Keywords: auditory efferent; impulsivity; nicotinic receptors; olivocochlear; selective attention.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maintained Spatial Learning and Memory Functions in Middle-Aged α9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit Knock-Out Mice.Brain Sci. 2023 May 12;13(5):794. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050794. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239266 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Attention to Visual Stimuli Using Auditory Distractors Is Altered in Alpha-9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit Knock-Out Mice.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 6;36(27):7198-209. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4031-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27383594 Free PMC article.
-
Corticofugal and Brainstem Functions Associated With Medial Olivocochlear Cholinergic Transmission.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 27;16:866161. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.866161. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35573302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Corticofugal Effects of Auditory Cortex Microstimulation on Auditory Nerve and Superior Olivary Complex Responses Are Mediated via Alpha-9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit.PLoS One. 2016 May 19;11(5):e0155991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155991. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27195498 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor structure and function in the efferent auditory system.Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006 Apr;288(4):424-34. doi: 10.1002/ar.a.20302. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16550589 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of α-9 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit Predominantly Results in Impaired Postural Stability Rather Than Gaze Stability.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 13;15:799752. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.799752. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095424 Free PMC article.
-
The Strength of the Medial Olivocochlear Reflex in Chinchillas Is Associated With Delayed Response Performance in a Visual Discrimination Task With Vocalizations as Distractors.Front Neurosci. 2021 Dec 9;15:759219. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.759219. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955720 Free PMC article.
-
The olivocochlear reflex strength in awake chinchillas is relevant for behavioural performance during visual selective attention with auditory distractors.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 10;10(1):14894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71399-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32913207 Free PMC article.
-
Maintained Spatial Learning and Memory Functions in Middle-Aged α9 Nicotinic Receptor Subunit Knock-Out Mice.Brain Sci. 2023 May 12;13(5):794. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050794. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239266 Free PMC article.
-
A review of efferent cholinergic synaptic transmission in the vestibular periphery and its functional implications.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Feb 1;123(2):608-629. doi: 10.1152/jn.00053.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 4. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31800345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chudasama Y., Passetti F., Rhodes S. E. V., Lopian D., Desai A., Robbins T. W. (2003). Dissociable aspects of performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task following lesions of the dorsal anterior cingulate, infralimbic and orbitofrontal cortex in the rat: differential effects on selectivity, impulsivity and compulsivity. Behav. Brain Res. 146, 105–119. 10.1016/j.bbr.2003.09.020 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

