Closed-Loop Hybrid Gaze Brain-Machine Interface Based Robotic Arm Control with Augmented Reality Feedback
- PMID: 29163123
- PMCID: PMC5671634
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2017.00060
Closed-Loop Hybrid Gaze Brain-Machine Interface Based Robotic Arm Control with Augmented Reality Feedback
Abstract
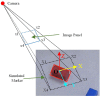
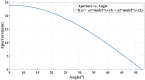
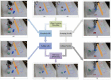
Brain-machine interface (BMI) can be used to control the robotic arm to assist paralysis people for performing activities of daily living. However, it is still a complex task for the BMI users to control the process of objects grasping and lifting with the robotic arm. It is hard to achieve high efficiency and accuracy even after extensive trainings. One important reason is lacking of sufficient feedback information for the user to perform the closed-loop control. In this study, we proposed a method of augmented reality (AR) guiding assistance to provide the enhanced visual feedback to the user for a closed-loop control with a hybrid Gaze-BMI, which combines the electroencephalography (EEG) signals based BMI and the eye tracking for an intuitive and effective control of the robotic arm. Experiments for the objects manipulation tasks while avoiding the obstacle in the workspace are designed to evaluate the performance of our method for controlling the robotic arm. According to the experimental results obtained from eight subjects, the advantages of the proposed closed-loop system (with AR feedback) over the open-loop system (with visual inspection only) have been verified. The number of trigger commands used for controlling the robotic arm to grasp and lift the objects with AR feedback has reduced significantly and the height gaps of the gripper in the lifting process have decreased more than 50% compared to those trials with normal visual inspection only. The results reveal that the hybrid Gaze-BMI user can benefit from the information provided by the AR interface, improving the efficiency and reducing the cognitive load during the grasping and lifting processes.
Keywords: augmented reality feedback; brain-machine interface (BMI); closed-loop control; eye tracking; human-robot interaction; hybrid Gaze-BMI.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Robotic arm control system based on augmented reality brain-computer interface and computer vision].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 25;38(3):483-491. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202011039. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34180193 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A scoping review of gaze and eye tracking-based control methods for assistive robotic arms.Front Robot AI. 2024 Feb 19;11:1326670. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1326670. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 38440775 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-Autonomous Robotic Arm Reaching With Hybrid Gaze-Brain Machine Interface.Front Neurorobot. 2020 Jan 24;13:111. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2019.00111. eCollection 2019. Front Neurorobot. 2020. PMID: 32038219 Free PMC article.
-
Blending of brain-machine interface and vision-guided autonomous robotics improves neuroprosthetic arm performance during grasping.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016 Mar 18;13:28. doi: 10.1186/s12984-016-0134-9. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 26987662 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Brain-machine interface-based training for improving upper extremity function after stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 3;16:949575. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.949575. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35992923 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integration of Augmented Reality and Brain-Computer Interface Technologies for Health Care Applications: Exploratory and Prototyping Study.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Apr 21;6(4):e18222. doi: 10.2196/18222. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35451963 Free PMC article.
-
The Advantage of Low-Delta Electroencephalogram Phase Feature for Reconstructing the Center-Out Reaching Hand Movements.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 15;13:480. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00480. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31156367 Free PMC article.
-
[Robotic arm control system based on augmented reality brain-computer interface and computer vision].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 25;38(3):483-491. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202011039. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34180193 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Closed-Loop Phase-Dependent Vibration Stimulation Improves Motor Imagery-Based Brain-Computer Interface Performance.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jan 25;15:638638. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.638638. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33568973 Free PMC article.
-
A scoping review of gaze and eye tracking-based control methods for assistive robotic arms.Front Robot AI. 2024 Feb 19;11:1326670. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1326670. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 38440775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreu-Perez J., Cao F., Hagras H., Yang G.-Z. (2017). A self-adaptive online brain machine interface of a humanoid robot through a general Type-2 fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2637403 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

