PPARgamma Deficiency Counteracts Thymic Senescence
- PMID: 29163553
- PMCID: PMC5681731
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01515
PPARgamma Deficiency Counteracts Thymic Senescence
Abstract
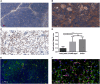
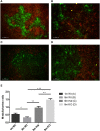
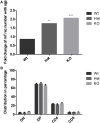
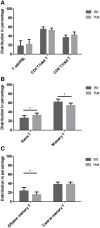
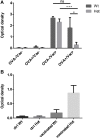
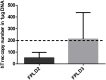
Thymic senescence contributes to increased incidence of infection, cancer and autoimmunity at senior ages. This process manifests as adipose involution. As with other adipose tissues, thymic adipose involution is also controlled by PPARgamma. This is supported by observations reporting that systemic PPARgamma activation accelerates thymic adipose involution. Therefore, we hypothesized that decreased PPARgamma activity could prevent thymic adipose involution, although it may trigger metabolic adverse effects. We have confirmed that both human and murine thymic sections show marked staining for PPARgamma at senior ages. We have also tested the thymic lobes of PPARgamma haplo-insufficient and null mice. Supporting our working hypothesis both adult PPARgamma haplo-insufficient and null mice show delayed thymic senescence by thymus histology, thymocyte mouse T-cell recombination excision circle qPCR and peripheral blood naive T-cell ratio by flow-cytometry. Delayed senescence showed dose-response with respect to PPARgamma deficiency. Functional immune parameters were also evaluated at senior ages in PPARgamma haplo-insufficient mice (null mice do not reach senior ages due to metabolic adverse affects). As expected, sustained and elevated T-cell production conferred oral tolerance and enhanced vaccination efficiency in senior PPARgamma haplo-insufficient, but not in senior wild-type littermates according to ELISA IgG measurements. Of note, humans also show increased oral intolerance issues and decreased protection by vaccines at senior ages. Moreover, PPARgamma haplo-insufficiency also exists in human known as a rare disease (FPLD3) causing metabolic adverse effects, similar to the mouse. When compared to age- and metabolic disorder-matched other patient samples (FPLD2 not affecting PPARgamma activity), FPLD3 patients showed increased human Trec (hTrec) values by qPCR (within healthy human range) suggesting delayed thymic senescence, in accordance with mouse results and supporting our working hypothesis. In summary, our experiments prove that systemic decrease of PPARgamma activity prevents thymic senescence, albeit with metabolic drawbacks. However, thymic tissue-specific PPARgamma antagonism would likely solve the issue.
Keywords: PPARgamma; immunity; rejuvenation; senescence; thymus.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

